Not a single cell of the human body can exist without phospholipids. These components are the basis of cell membranes. But sometimes due to certain functional disorders a malfunction occurs in the human body. And as a result of this, antibodies to phospholipids IgG and IgM begin to be produced. Such aggressive substances attack healthy cells, which causes the development of a very dangerous disease - antiphospholipid syndrome (APS).
What do abnormal results mean?
Myositis. . Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining blood may be more difficult for some people than for others. Other circulatory risks are mild but may include.
Excessive bleeding Fainting or feeling slightly hungry. . However, the test itself does not represent a diagnosis, but should be used in conjunction with your medical history, physical examination and other tests. Many people, even many doctors, haven't heard of antibody tests, which can help diagnose type 1 diabetes. These blood tests measure specific antibodies in body-related autoimmune activity that attack insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, Dr. Dr. Laurie Laffel, director of the section on diabetes for children, adolescents and young adults at the Yoslin Diabetes Center and professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School.
As a result of an increase in the amount of antibodies, the blood clotting process is disrupted. IN vascular system serious pathological changes. There is a narrowing of the lumens of blood vessels and, as a result, blood circulation worsens.
Clots form in the bloodstream, leading to blood clots. APS is manifested by the development of heart attacks and strokes in young people against the background of thrombosis. Women carrying a child experience spontaneous miscarriages or fetal death. Wherein:
There is no need to prepare for antibody testing. There are five types; each of which measures different antibodies. To test for peptide C, you must fast. More than one test can be performed because any one of them may have negative result for type diabetes.
Because levels of this peptide usually correspond to insulin levels in the body, the test can indicate how much insulin the body is producing. Low C-peptide and insulin levels usually indicate type 2 diabetes against glutamic acid decarboxylase. This test examines antibodies against a specific enzyme in the beta cells of the pancreas that produce insulin. In addition to beta cell attacks the immune system In people with type 1 diabetes, insulin is also affected, Laffel said. This test examines antibodies against insulin. Autoantibodies associated with insulinoma 2. This test looks for antibodies against a specific enzyme in beta cells. This assay looks at the reaction between islet cell antibodies and various islet cell proteins from the animals' pancreas, Laffel said. If your antibodies react with animal islet cells, you have a marker for type 1 diabetes. This is the oldest test for type 1 antibodies and is hardly used today. Zinc Transporters - The most recent test for type 1 diabetes detects antibodies against a specific beta cell enzyme. This analysis is not universally available. Anti-insulin autoantibodies. . What is serology and what is it used for?
- IgG antibodies to phospholipids indicate chronic forms of diseases in the human body.
- Ab to phospholipids IgM indicates acute form diseases.
What kind of analysis is this
It is impossible to independently understand that the human body produces antibodies to phospholipids. Illness and health problems are usually explained by viral infection or dysfunction of certain organs and systems. In this regard, to determine the amount of antibodies, it is necessary to do a blood test in a specialized laboratory.
In this message we called Serology, we want to clearly and concisely tell you all the information we are interested in about this type of analytics, what is it? and what data may be obtained based on the results. Serology is the study of serum. Serum is the part of the blood that, after coagulation, continues to maintain its original liquid state. We usually usually hear the word "serum" associated with blood, and the reason is that it is a very common type of analytics when detecting an infectious process.
Based on a blood test for antibodies to phospholipids (class IgG and IgM), specialists obtain an important indicator that allows timely diagnosis of a severe autoimmune disorder. Thanks to this, it is possible to prescribe the correct treatment in a timely manner and eliminate serious complications.

How is a serological test performed?
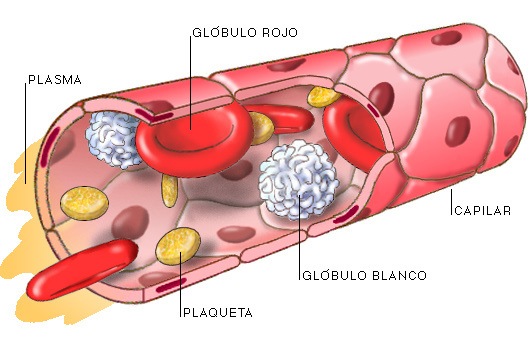
By studying blood serum, the presence of antibodies can be diagnosed, providing a reliable way to know the body's response to an infection or pathogen. Serum tests can analyze both serum and the rest of the blood. To perform serum analysis, once the blood is clotted and the liquid serum is left, the centrifugation process is applied again to both the coagulated blood and the serum. This makes it much easier to identify and predict possible diseases.
In the process of examining blood plasma, the doctor determines the presence of antibodies to the following types of phospholipids:
- Negatively charged - phosphatidylserine, cardiolipin.
- Positively charged - phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylic acid.
- Neutral - phosphatidylcholine.
When is the test ordered?
A blood test is prescribed for:
Why is serology performed?
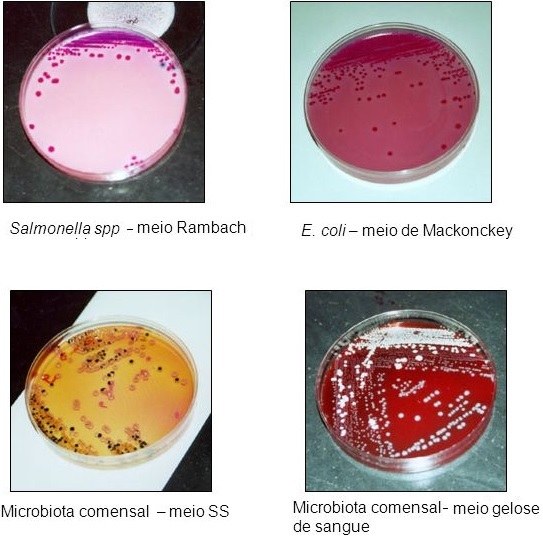
Among the diseases that can be detected using serological testing are rubella, anthrax, brucellosis, viral hepatitis or AIDS, some of the diseases that can generate antibodies. Rule out the presence of antibodies in the blood. A doctor may suspect an infection if a person has been exposed to risk factors.
In other cases, the person is not sick, but they have latent antibodies to certain diseases. The physician may request serology in advance. For example, if a woman is about to undergo treatment, the doctor will ask for serology to check for an underlying disease that could be passed on to the baby.
- obstetric pathologies, which are manifested by constant spontaneous abortions, premature births, developmental delay or fetal death later pregnancy.
- hematological disorders associated with the diagnosis of thrombocytopenia.
- diseases of the pulmonary system, namely: pulmonary embolism, thrombotic pulmonary hypertension, as well as pulmonary hemorrhage.
- cardiovascular pathologies, such as myocardial infarction, damage to the heart valves, abnormal rhythms of the heart muscle or arterial hypertension.
- pathologies of the nervous system associated with circulatory disorders, which are characterized by headaches, various mental disorders and convulsions, as well as strokes.
- the development of liver diseases, in particular with liver infarction, hepatomegaly and an increase in the concentration of liver enzymes.
- development of kidney diseases such as renal infarction or chronic renal failure.
- various vascular pathologies and bleeding of unknown origin.
- thrombosis, thrombophlebitis and gangrene of unexplained etiology.
- systemic lupus erythematosus.

Some serology tests don't limit themselves to analyzing a blood sample; they also analyze semen or saliva. In a forensic investigation, serological tests are used to confirm whether there is a link between a test found and an alleged suspect, such as an alleged rapist and a semen sample found. Antibodies are very useful in forensic investigations; a blood sample containing certain antibodies can be a source of information to rule out suspects or lead new lines of investigation.
The following diseases can provoke the production of antibodies in the blood:
- Oncological diseases.
- Tuberculosis.
- Staphylococcal and streptococcal infections.
- Herpetic infection.
- Measles.
- Rubella.
- Mononucleosis.
- Mycoplasma.
- Allergic reactions.
Certain types of antibodies can promote the production of antibodies in the body. medications antiarrhythmic and psychotropic effects. Hormonal contraceptives, novocaineimide and quinidine are also dangerous. Various toxic substances also have a provoking effect.
How is serology performed?
The procedure is similar to when you drew blood at a different time, you won't notice anything different or draw more blood. The blood is placed in a sterile vial, which must be tested in a laboratory. 
The laboratory will determine how certain antibodies react to the presence of specific antigens, so you can find out which antibodies are which.
Serology of sexually transmitted diseases
There are several different methods used in serology to analyze these antibodies. 
As we have already indicated, serology is carried out in order to determine whether the blood contains a sufficient amount of antibodies, or in other words, if the normal values have been changed by a bacterium that will later lead to a disease which, if it can be treated effectively and quickly, it also may be difficult if not provided before the disease is advanced.
Preparing for analysis
The guarantee of the reliability of the information received is proper preparation to donate blood. The main rules are as follows:
- Venous blood is collected in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Before donating blood, it is recommended to follow a diet for a couple of days. The diet should include only non-fatty boiled dishes. It is necessary to give up coffee, carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
- You cannot donate blood for analysis if a person is prescribed treatment for diseases with special medications.
- It is not recommended to take blood samples to determine antibody levels after a physiotherapy session.
How is the analysis carried out?
If the initial study of blood plasma reveals IgG and IgM antibodies to phospholipids, then a repeat test is required after 8-12 weeks to confirm the diagnosis. Results for antibody levels can be obtained one day after blood collection.

Something very important to consider is that although the symptoms of these diseases are usually very specific and deterministic, in many cases the disease is suffered without many of them or even with any type of pain or at least in early stages diseases.
This usually makes a person believe that he is in a very good condition, without any problems for which he should worry, in turn, this leads to blind trust in a false approach, which in many cases turns out to be the cause of the underlying disease of severe diseases with subtle forecast.

Repeated blood testing is necessary due to the fact that in acute infectious and inflammatory diseases of a bacterial or viral nature, a sharp jump in antibodies in the blood is always observed. As a rule, the infection can be overcome within 1-3 weeks. But if this does not happen, then it will again be detected in the blood a large number of antibodies. And this is most likely a sign of the development of APS.
If we notice any symptom that makes us suspicious, we should carry out the appropriate tests. We all know how to add two and two, and if we see something unusual or unusual happening in our genital area, we will pay close attention to whether it is a one-day, one-time or frequent occurrence, if ever happened to us, or if accompanied by other symptoms that do not seem to be related.
For example, fever can be a symptom of many diseases and is very diverse, although for simplicity we include it in infections, regardless of type. This means that a stomach infection can trigger vomiting, the flu can cause sneezing and mucus buildup, as well as sexual discomfort, pain and swelling in the affected area. However, each case should be treated differently so that fever is not the defining symptom.
Acceptable indicators
Normally, antibodies to phospholipids in the blood plasma are practically absent or contained in a minimal amount that is of no diagnostic value. Indicators up to 10 units/ml exclude the presence of antiphospholipid syndrome.
With an increased amount of antibodies, changes in other important indicators in the blood serum occur. This is revealed when carrying out general analysis blood, the results of which reflect:
However, if a person is bleeding from the penis, or any person feels a certain burning sensation in the area, as well as discomfort when urinating or high sensitivity, it is very possible that it is something important. That this value can be immediately reduced when treatment begins and goes no further, but if it is not given the importance it deserves, it can be difficult, and in addition to becoming more dangerous and annoying, the more difficult or it will be more difficult to solve.
Normal values in serology
Performing serology in these cases can be very helpful, especially if unprotected sex is suspected. When this happens, antibodies are usually not found in the blood sample. 
Abnormal values in serology
In this case, the presence of antibodies was detected in a blood test. The detection of antibodies in the blood can be caused.- Increase in ESR.
- Decreased platelet levels.
- Increased white blood cell count.
Against the background of the presence of antibodies, the biochemical blood test will also display:
- Increased gamma globulin levels.
- In case of renal failure - increased levels of urea and creatinine.
- With the development of liver pathologies - an increase in the level of ALT and AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin.
- Increased aPTT during blood clotting tests.
Deviation of results from the norm
Low or moderate levels of antibodies in the blood serum most often indicate the use of medications. A pathology is considered if the concentration of antiphospholipid antibodies remains at high level for a long time, which is confirmed by repeated analysis. The diagnosis of APS is made against the background of specific clinical manifestations, if the presence of antibodies in the blood serum is confirmed. This is very dangerous disease, which has not yet been fully studied.
- Was infected in the past.
- Now the person is suffering from active infection.
- The virus or microorganism is latent and may develop later.
Infections that can be detected by serology
If a doctor suspects a person is suffering from the disease, they will likely ask for another serology about 10 days after the first test. It is clear that in order for us to ask for this test, we must have reasons for doctors to ask us. This is a test that is done in many cases to find out if we have any infection or if we are suffering from one and if we have antibodies in the blood. We will list all the infections that can be detected using this test so that we can see its great value.

During pregnancy, the disease warns of a high risk of complications during pregnancy. A dangerous consequence Antiphospholipid syndrome is thrombosis of placental vessels.
Against this background, various gynecological pathologies arise. Such a diagnosis made during pregnancy is especially dangerous. It indicates that a woman may experience spontaneous miscarriage at any time, but most often, fetal loss occurs in the second and third trimesters.
Women diagnosed with APS are at risk of infertility, and even if they manage to become pregnant, the risk is high intrauterine death fetus or premature birth. The clinical manifestation of increased antibodies is constant spontaneous miscarriages.
Clinical picture
With APS, clinical manifestations can vary, and the overall picture depends on the following factors:
- Sizes of damaged vessels.
- Vessel occlusion rates.
- Functional purpose of blood vessels.
- Location of blood vessels.
The following changes may be observed on skin surfaces during APS:
- Vascular network on the hands and feet.
- Rash in the form of dots.
- Presence of subcutaneous hematomas.
- Long-term non-healing ulcerative lesions of the skin surfaces.
- Subcutaneous nodules.
An increase in antibodies always warns of the possible development of thrombosis. In this case, damage can affect any vessels, but the most common is venous thrombosis. Thrombi are most often localized in the deep veins of the lower extremities, but sometimes such pathologies affect the hepatic, portal or superficial veins.
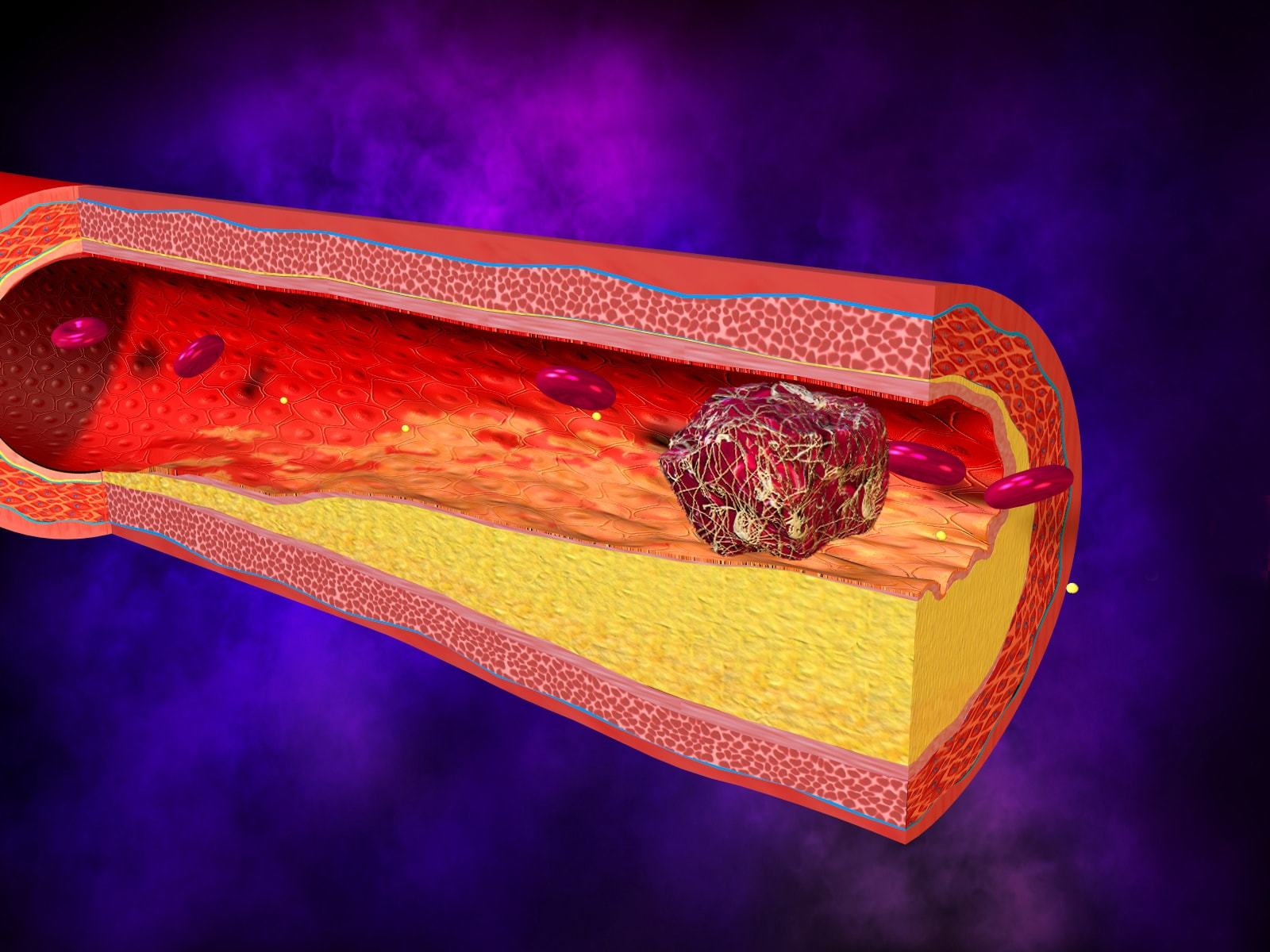
Against the background of damage to the blood vessels of the lungs, pulmonary hypertension often develops. Thrombosis of the main vein of the adrenal glands with the further occurrence of hemorrhages and infarction contributes to the occurrence of adrenal insufficiency.
Blood clots in the arteries that occur during aPL are most dangerous for the vessels of the brain. This most often leads to a stroke. And such dangerous pathology very often affects people at a young age, without any predisposing factors.
The prognosis for APS is ambiguous. The success of treatment depends on many factors. First of all, it is important to promptly donate blood for testing to determine the level of antibodies. Only on the basis of the results of blood tests and clinical manifestations can the correct treatment be prescribed by a rheumatologist. But it should be borne in mind that consultation with many specialists will be necessary, due to the fact that this disease affects many organs.
A blood antibody test is prescribed to determine the patient’s immune status. Antibodies are specific proteins whose function is to bind antigens, forming poorly soluble complexes with them. Antibodies are produced by lymphocytes. The presence of antibodies to infectious pathogens or their toxins indicates past infections or a developing infection. Antibodies to infectious antigens help identify viruses or bacteria that cannot be detected by other methods. Antibodies are divided into five classes: IgA, IgE, IgM, IgG, IgD.
Antibody testing may be performed to detect the following: infections: viral hepatitis, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, chlamydia, leptospirosis, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, clostridial infection (tetanus), diphtheria, whooping cough, syphilis, HIV.
Availability autoantibodies becomes a decisive factor for establishing the diagnosis of an autoimmune disease. Autoantibodies are formed to the body’s own antigens: phospholipids, DNA fragments, hormones or receptors. Autoantibody testing:
- Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase
- Antibodies to TSH receptors
- Antibodies to thyroglobulin
- Antibodies to double-stranded DNA (a-dsDNA)
- Antibodies to single-stranded DNA (a-ssDNA)
- Antibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA)
- Antibodies to phospholipids
- Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA)
- Antibodies to liver and kidney microsomal fraction (LKM)
- Antibodies to transglutaminase IgA
- Antibodies to transglutaminase IgG
- Antibodies to pancreatic β-cells
- Antibodies to insulin
- Antibodies to glutamate decarboxylase (GAD)
- Antisperm antibodies
- Antiovarian antibodies
- Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (Ab to CCP)
- Antibodies to modified citrullinated vimentin
Availability antisperm And antiovarian antibodies are the cause of infertility. Antibodies to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptors can lead to thyrotoxicosis . Antibodies to thyroglobulin are the cause of autoimmune inflammation of the thyroid gland. Antibodies to insulin cause insulin resistance and development diabetes mellitus. Antibodies to Rh factor help predict the risk of Rh conflict in repeated pregnancies.
Determination is of great importance in laboratory diagnostics. rheumatoid factor(for rheumatoid arthritis ), antinuclear antibodies(with lupus erythematosus), antibodies to acetylcholine receptors(for myasthenia gravis), to double-stranded DNA(with systemic lupus erythematosus).









