Enthusiasts interested in how to grow bonsai from seeds should know that this path is the longest, but also rewarding. Here, a person has control over the plant literally from the moment the seed is pecked, and it is easier to change the shape of the shoots and roots because of their flexibility.
It is not necessary to choose an exotic type of tree or shrub. The main thing is that the plant has small leaves and small annual growth, otherwise it will be much more difficult to “tame” the future bonsai tree.
Choosing the right tree for bonsai
What types of plants are suitable for bonsai, tree in Japanese style? To quickly get an attractive tree, you can pay attention to:
The choice of trees suitable for bonsai is incredibly large, and many of them are indigenous to Russia and are found in gardens, parks, city squares and forests. Magnificent compositions are obtained from serviceberry, hawthorn, acacia and birch, elderberry and linden, euonymus and oak.
Before growing a bonsai, based on the type of plant, its future height and style are determined.
How to grow bonsai from seeds?
 Seeds of trees and shrubs suitable for bonsai are divided into two types. Some crops are immediately ready for germination, but the evolutionary “program” of many species includes a period of hibernation, when the sprout waits out the cold season. At home, stratification will help imitate winter.
Seeds of trees and shrubs suitable for bonsai are divided into two types. Some crops are immediately ready for germination, but the evolutionary “program” of many species includes a period of hibernation, when the sprout waits out the cold season. At home, stratification will help imitate winter.
Tree seeds for Japanese bonsai are placed in damp sand or sphagnum moss for 3–5 months, after which the container is placed in the refrigerator. At a slightly positive temperature in a humid environment, the seed prepares for growth. When it is transferred to warmth, the sprout quickly awakens. For evergreen species and plants with seeds that have a particularly durable shell, heat or temperature contrast is used to awaken.
Sowing of seeds is carried out from spring to early autumn. Seedlings obtained in the second half of summer already need lighting, which is simply irreplaceable in autumn and winter.
For germination and the first months of seedling life, a light sand-peat substrate or peat tablets that have been soaked and absorbed moisture are used. Until a sprout appears on the surface, the container should be kept in the dark under the film. The air temperature is selected depending on the bonsai tree being grown.
 To avoid the formation of condensation and rot, the greenhouse is ventilated. When shoots appear, little access is provided inside fresh air and transfer the seedlings to the light. As necessary, seedlings are watered and fertilized with complex compounds. When the plant reaches a height of 10–12 cm, it is replanted.
To avoid the formation of condensation and rot, the greenhouse is ventilated. When shoots appear, little access is provided inside fresh air and transfer the seedlings to the light. As necessary, seedlings are watered and fertilized with complex compounds. When the plant reaches a height of 10–12 cm, it is replanted.
 At this stage, the main root is shortened by a third to slow down the vertical growth of the tree. They immediately begin to form the future trunk, for which they use copper wire.
At this stage, the main root is shortened by a third to slow down the vertical growth of the tree. They immediately begin to form the future trunk, for which they use copper wire.
Choosing a pot and soil for bonsai
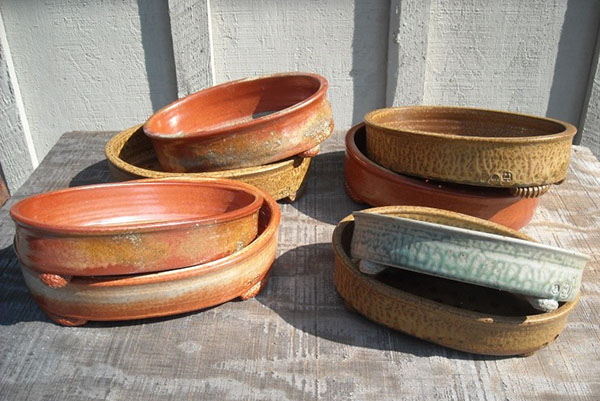 It is not for nothing that the bonsai tree is called tray-grown. To limit the pet’s growth, it is planted in a deliberately small and shallow container, while simultaneously forming and cutting off part of the root system.
It is not for nothing that the bonsai tree is called tray-grown. To limit the pet’s growth, it is planted in a deliberately small and shallow container, while simultaneously forming and cutting off part of the root system.
When choosing a bonsai pot, you need to take into account that over the years the tree becomes heavy and, especially with an irregular, inclined or cascading shape, may lose stability. Therefore, for bonsai ranging in size from a few centimeters to 9 meters, massive, often ceramic pots, bowls or containers of the most different forms and styles.
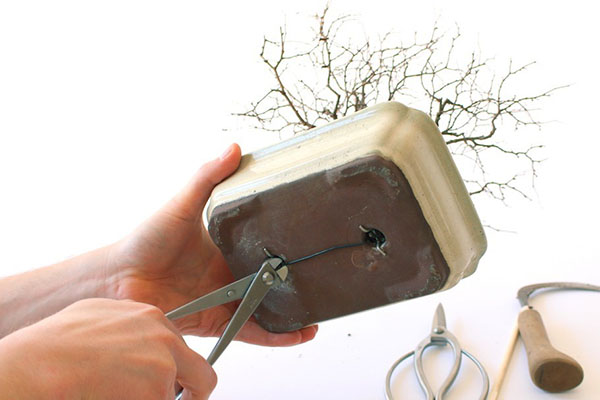 There should be a drainage hole at the bottom of the container and more than one. They are used not only to drain water, but also to secure the plant.
There should be a drainage hole at the bottom of the container and more than one. They are used not only to drain water, but also to secure the plant.
Secure the plant and protect it from fungal infection The root system will be helped by treating the bonsai pot with a hot solution of potassium permanganate or scalding with boiling water.
Bonsai soil is not only designed to provide the plant with nutrition and retain moisture, it should help the roots to gain a foothold in the relatively small volume of the pot. Therefore, for miniature copies of real oaks, lindens, lemons, maples and other trees, a special substrate is used.
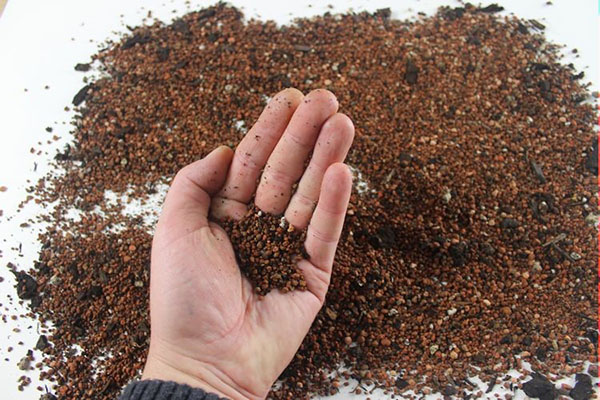 In Japan, for many centuries, such a mixture based on certain types of clay is called akadama. For greater nutritional value and looseness, fertile soil and sand are added to the granular substance:
In Japan, for many centuries, such a mixture based on certain types of clay is called akadama. For greater nutritional value and looseness, fertile soil and sand are added to the granular substance:
- For deciduous bonsai trees, a substrate containing 7 parts of turf soil and 3 parts of coarse washed sand is recommended.
- Flowering crops are grown on a mixture of 7 parts turf soil, three parts sand and 1 part highly nutritious humus.
- Conifers, the most popular among bonsai lovers, need particularly loose soil, for which take 3 parts turf soil and 2 parts washed sand.
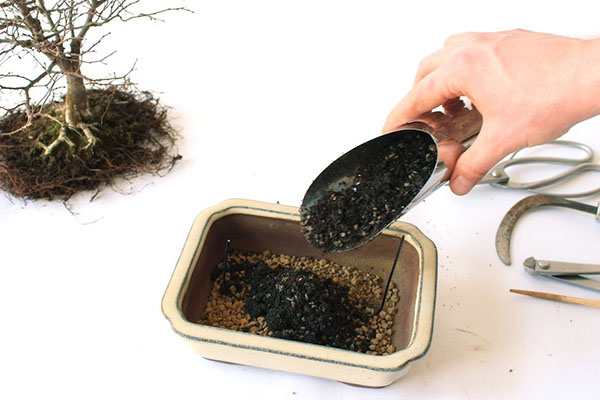 Before filling the pot, the bonsai soil is sorted out, removing foreign matter that could damage the roots, sifted and sterilized. A drainage layer is placed at the bottom of the container to drain excess moisture.
Before filling the pot, the bonsai soil is sorted out, removing foreign matter that could damage the roots, sifted and sterilized. A drainage layer is placed at the bottom of the container to drain excess moisture.
Caring for a bonsai tree at home
 It is not enough to purchase a miniature tree, get a young seedling, or root a cutting of the species you like. It is important to know how to care for a bonsai tree.
It is not enough to purchase a miniature tree, get a young seedling, or root a cutting of the species you like. It is important to know how to care for a bonsai tree.
By constantly limiting growth, shaping the crown and growing a bonsai in a small pot, a person completely changes the life of a tree or shrub. Therefore, caring for such a crop is very different from caring for other indoor plants.
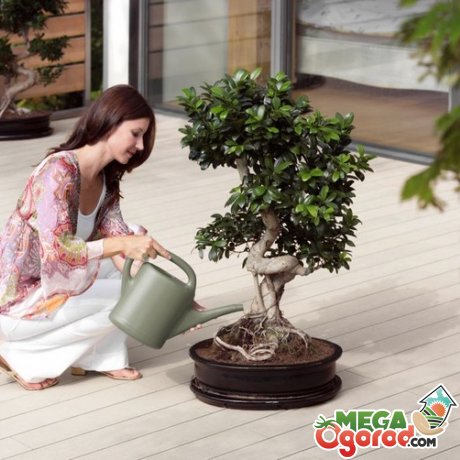
The main task of the gardener is to organize watering of the bonsai, which is not easy to cope with with a small volume of soil and a shallow pot filled with roots.
Previously, gardeners only had at their disposal a specially shaped watering can or the ability to immerse a bonsai pot in a bowl of water to wet the soil from below. Today, plant irrigation or drip irrigation is actively used, which allows the soil under bonsai to be moistened in doses and without the risk of erosion.
 For irrigation, use only soft, melted or settled water. During the growing season, plants need more moisture; with the onset of autumn and the approach of the dormant period, watering is reduced and carried out less frequently, focusing on the condition of the substrate.
For irrigation, use only soft, melted or settled water. During the growing season, plants need more moisture; with the onset of autumn and the approach of the dormant period, watering is reduced and carried out less frequently, focusing on the condition of the substrate.
Feeding is carried out at intervals of 2–3 weeks, using your own mixtures for different cultures and seasons. For Japanese bonsai trees, there are mineral fertilizers based on algae.
You can’t leave plants without food, but it’s equally important not to overfeed your bonsai. Therefore, when caring for bonsai trees at home, fertilizing is done very carefully:
- in the spring, at maximum growth intensity, including twice as much potassium and phosphorus in the fertilizer;
- in summer the proportions remain the same, but the concentration is halved;
- closer to autumn, especially for deciduous crops, the content of potassium and phosphorus is doubled, and nitrogen, on the contrary, is reduced.
- Flowering and fruit-bearing trees and shrubs need more potassium, which is used for the formation of buds and ovaries.
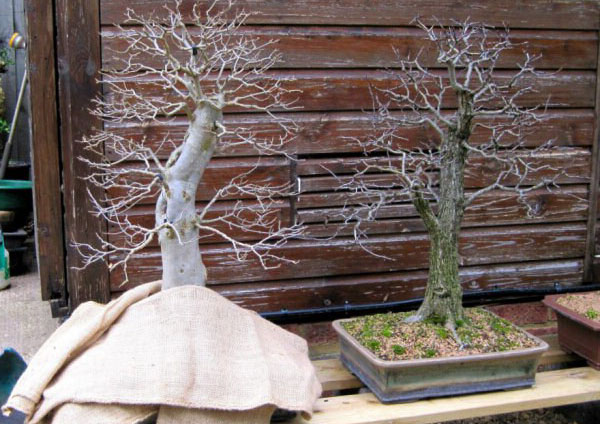 With the arrival of winter, nothing changes for exotic evergreens, but coniferous and deciduous trees must prepare for winter. How to care for a bonsai tree in winter? If the climate allows, they are left outside or brought onto unheated terraces. The root system in a small bonsai pot may be the first to suffer, so it is additionally covered and the soil is dried a little. With the onset of spring, the plant awakens and again needs watering, fertilizing and the formation of the crown and roots, which is mandatory for bonsai.
With the arrival of winter, nothing changes for exotic evergreens, but coniferous and deciduous trees must prepare for winter. How to care for a bonsai tree in winter? If the climate allows, they are left outside or brought onto unheated terraces. The root system in a small bonsai pot may be the first to suffer, so it is additionally covered and the soil is dried a little. With the onset of spring, the plant awakens and again needs watering, fertilizing and the formation of the crown and roots, which is mandatory for bonsai.
How to grow bonsai - video
Video about the bonsai exhibition
盆栽 lit. "grown in a tray") is the art of growing an exact replica of a real tree in miniature. The word "bonsai" comes from the Chinese "pen-tsai". Art arose in 231 BC. e. in China.
Story
The first reliable written sources concerning the emergence of the bonsai style come from China and date back to the Tang Dynasty (VIII-X centuries), where the image first appeared in wall painting penzai- a plant taken from nature and then transplanted into a pot. These plants were cultivated by Buddhist monks probably several centuries BC and subsequently became one of the occupations of the local nobility.
Styles
Currently, the following bonsai styles exist:
| Chokkan | Formal Straight Style (Tekkan) - In this traditional style, the trunk remains straight, thickening at the root. | |
| Moyogi |  |
A tree grown in the informal upright style (moyogi) may have slightly crooked branches or trunk. The top of the trunk is always in a straight line extending perpendicular to the ground where the root begins. |
| Sokan |  |
Sokan (“double trunk”) - is a composition that differs from the others in the presence of two trunks. They can be different in size and form one crown. |
| Shakan |  |
The inclined style (shakan) differs from the formal straight style only in that the tree grows at an angle to the ground. |
| Kengai |  |
The cascade (kengai) imitates the growth of trees near water or on mountains. In a full cascade, the top of the tree grows beyond the border of the pot and falls well below the soil in the pot. |
| Han-Kengai | Han-kengai - semi-cascade style. In a semi-cascade, the rising top of the tree remains at the level of the soil of the bowl. | |
| Netsunagari | Netsunagari is a style that imitates the appearance of trees in which part of the trunk is flooded or covered with earth. The branches of such a plant grow, resembling individual trees. | |
| Bunjingi (literary style) |  |
The “pundit style” is characterized by a straight tree trunk, with a minimum of branches. |
| Sekijoju |  |
Sekijoju - “root on a stone” - a tree (often a fig) grows on a stone. The trunk is located directly on the stone, and the roots intricately entwine it. |
| Ishizuki |  |
Ishizuki or "growing-on-rock" style is similar to sekijoju style, but in this case the roots of the tree grow in the crevices of the stone. Since there is little room for roots, this style is used to illustrate the tree's hardiness. |
| Hokidachi |  |
Hokidachi - "Broom Style" - used on trees with spreading branches. The trunk remains straight and the branches grow around it to about 1/3 of the height of the tree, causing the leaves to form a ball-like shape. |
| Yose Ue (Youse-Ue) | "Yose Ue", or group of trees, is a style in which more than 9 trees are grown in one composition. Their number can vary, but almost never equals 4 (the word “si”, “four”, in Japanese sounds like the word “death”). Often trees of the same species are planted in a pot, and the beauty of the composition lies in the combination of heights and ages of these trees. | |
| Ikadabuki | The multi-trunk style, ikadabuki (raft-shaped style), is distinguished by the fact that it imitates a tree that has fallen in a swamp; the base is shaped like a raft and is formed by a trunk lying on the ground, from which trees of different sizes grow. |
Size classification
Agricultural technology
Watering
Due to the limited size of the plant's pot, caring for a bonsai can be quite challenging. Deep containers often do not allow the root system to develop properly, and watering such a plant turns into hard work. Various techniques Watering involves either direct irrigation from a watering kettle or jar, or immersing the bonsai container in a large container filled with water. Some plant species can tolerate periods of drought, while others require almost constant watering. If you leave the soil dry or water it too often, its root system may die. Sun and wind can quickly dry out the soil, so plants outside should be checked daily and watered when needed. The soil should not become dry at all, even short term. Some plants used in bonsai do not show a lack of water in the soil, remaining green even when their root system has completely died.
Maintaining air humidity
To maintain the required level of humidity, plants are sprayed several times a day, while dust particles are washed off from the leaves.
Often, to imitate grass, the soil surface is covered with moss, which requires daily spraying and high air humidity.
Transfer

Transplanting a plant
Bonsai are usually replanted approximately every two years in the spring, just before they begin to flow sap after hibernation. The younger the plant, the more often it is replanted. This prevents roots from growing around the inside of the pot and promotes growth.
When replanting, some of the roots are cut off.
Also, replanting is a necessary remedy for rotting roots. The plant is removed from the bowl, damaged roots are inspected and removed.
Formation
There are various methods to reduce the size of a tree. Seasonal pruning is often the key to success, but if done incorrectly, it can destroy the tree. Most types of trees suitable for bonsai can be deformed using copper or aluminum wire. Some trees do not lend themselves to such shaping; their appearance is changed mainly through pruning. To create the appearance of an old tree, sometimes dead trees, “jin” and “shari” are used. They are obtained by cutting a branch from the trunk of a living tree and stripping the bark from all or part of the trunk (syari), creating the appearance of natural scars on the tree. These methods must be used with great care because such actions can lead to infection of the tree. Also, you cannot rip off a whole ring of bark from the trunk, otherwise the sap flow in the tree will be disrupted.
Dressing
Ligature is a wire with which the shoots are given the necessary direction. Tree ligation is one of the most strong ways tree shape control. Best time for dressing - spring and autumn. Sometimes weights are suspended from the branches to create bends and knots and an aged effect. Although ligation with wire is carried out very tightly, the wire should under no circumstances grow into the tree:25. Remove the wire by cutting it into small pieces, and not just unwinding it.
The thickness of the wire should be proportional to the thickness of the branch. Instead of very thick wire, you can use a pair of thinner twisted wires. Crossing wires should not be allowed. It is better to gradually braid the trunk from the bottom up over several months.
Trimming
Pruning is a necessary way to shape a bonsai. With its help, they solve several problems: they reduce the size of the plant, shape the arrangement of skeletal branches, and stimulate the growth of new shoots.
There are several types of pruning.
- Formative pruning - cutting out large skeletal branches, truncation of the trunk, forming the “base” of the tree
- Pruning branches reduces their length and stimulates the formation of new growth points and stimulates branching.
- Trimming the shoots forms the outline of the plant crown
- Pinching (pinching) serves to limit shoot growth
- Pruning leaves (defoliation) serves to renew the crown, while the number of leaves increases and their size decreases
- Root pruning is necessary to renew and form the root system
Split
Sometimes, to give the plant more ancient look, its trunk is split. In this case, part of the plant may die.
Shaping the trunk thickness
To give the plant the proportions of an adult tree, sufficient trunk thickness is necessary; obtaining a thick trunk is one of the most common tasks when creating bonsai. The following methods exist:
|
|
|
|
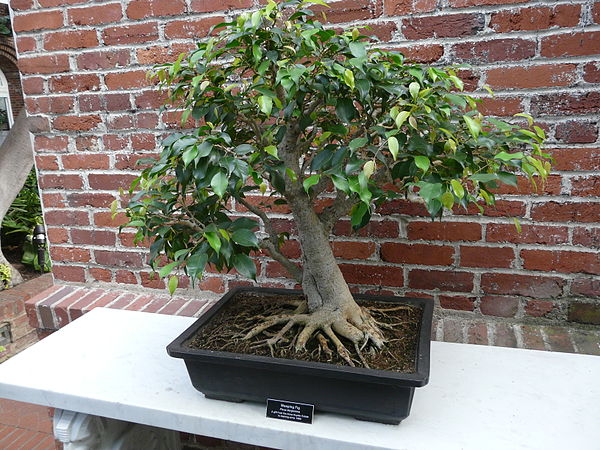
| Indoor Ficus Benjamin | Ficus benjamina grown as a bonsai | Ficus benjamina in natural conditions |
Dead wood
Top dressing
Location and wintering
Some trees require special protection in winter, and the intensity of the techniques used in cold weather depends primarily on how adapted the tree is to the climate. If a plant has a period of hibernation, then under no circumstances should it be interrupted, especially in deciduous plants. To protect the plant from the cold outside, you can place it in an additional container or cover the soil in the pot with a layer of humus reaching up to the first branch.
The technique of cultivating miniature trees originated in China over a thousand years ago. Bonsai literally means "plant on a tray." To Japan this technique came with Buddhist monks who used small trees to decorate the niches of houses, so the plants were no more than 50 cm. And in the 18th century, the Japanese turned this technique into a real art, and therefore a variety of styles arose.
Bonsai can be bought, but the pleasure is not cheap. Therefore, flower growers are increasingly practicing the cultivation of such trees on their own. In order for the idea to be crowned with success, you must first decide on the type of plants suitable for growing on a “tray”.
Bonsai species diversity
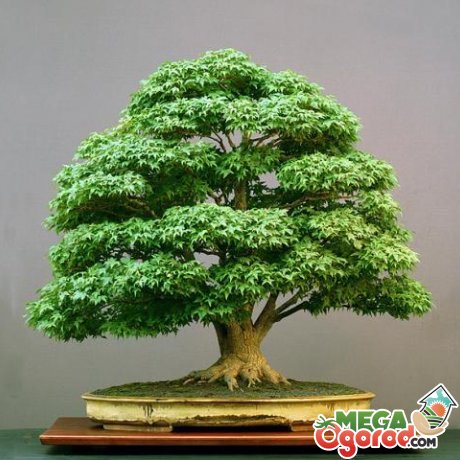

The species diversity of bonsai is extensive, but novice gardeners are recommended to start with coniferous plants, because they are long-lived and quite unpretentious.
There are several main types of bonsai that combine certain types of plants:
- evergreens that delight with rich greenery at any time of the year
- spring bloomers, which bloom during the spring months
- blooming in summer
- capable of producing flowers only in autumn
- with an intricate shape of the trunk and branches that are revealed to the eye after the leaves fall
You can use any plant for bonsai, but for indoor floriculture you should choose heat-loving trees and shrubs. Most often in apartments and offices you can admire the following views:
- dwarf pomegranate
- Ixoroi
- acacia
- bougainvillea
- , or firs
- fruit representatives of the garden, among which are, or
- oaks
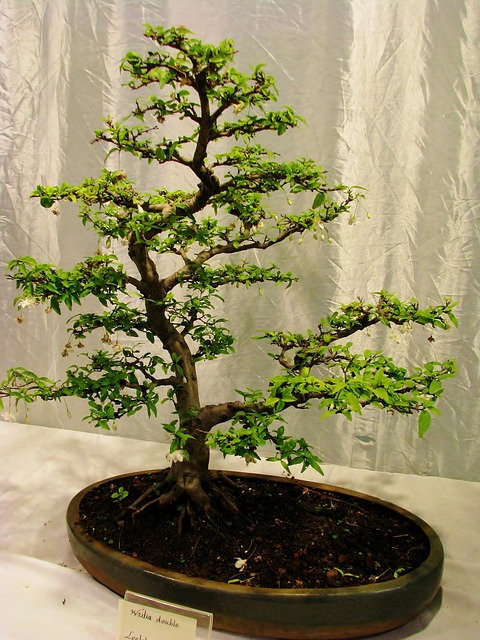
Some craftsmen also use more fastidious representatives of green nature to create bonsai. For inexperienced craftsmen who decide to grow a miniature forest or garden at home, any seeds of undemanding plants will do. Wisteria is often used, the small flowers of which densely cover the branches and make the plant very decorative.
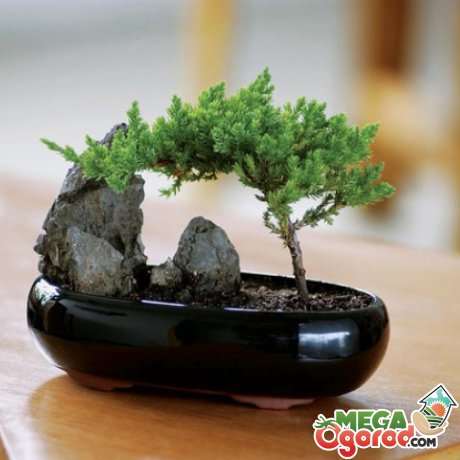

The secret to creating a small replica of a garden tree is to constantly trim the crown. In order to grow bonsai from seeds at home, you will need a lot of patience and great desire. You may not succeed on the first try, so you will have to start all over again.
The process of growing a miniature plant is quite long and requires constant attention.
Conventionally, the bonsai cultivation technique can be divided into three main stages:
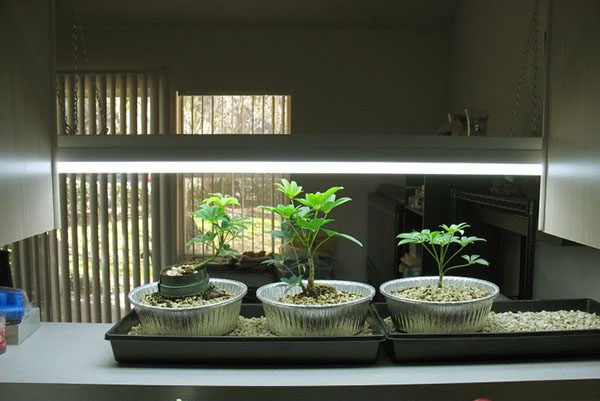
- Caring for the seed for a long time, which can last for years. The plant should be selected taking into account the climatic conditions of the region. Ficus and pine are considered the most adaptable.
- Taking care of the sprout. The most crucial moment that requires tireless attention. A young plant needs to be ventilated often. And when four full-fledged leaves appear, the sprout should be replanted and after two months, fertilizing should begin. In winter, it is advisable to move the plant to the windowsill and gradually reduce fertilizing.
- Maintenance of an adult tree. It is necessary to constantly monitor the degree of illumination and maintain an optimal level of humidity through periodic spraying. After a certain period of time, bonsai begins.
It is important to create optimal conditions for little green friends, especially on early stages growth. To do this, you should study the characteristics and preferences of the chosen culture and satisfy all its whims.

The secret to making bonsai decorative is that the trees need to be grown in a permanent container and the crown and roots must be trimmed periodically. Thanks to such segments, a balance is achieved between the above-ground and underground parts of the plant, and the desired crown is formed. In addition to pruning, other equally important cultivation conditions should be taken into account.
Care Tips:
- Accommodation. If you choose the right type of plant, you can grow it both indoors and outdoors. The main thing is to provide a sufficient amount of light and periodic ventilation. It is also necessary to remember that some crops have a rest period. These include decorative maple or. Some types of plants should first be kept indoors and then transplanted into the garden. Experienced gardeners claim that there are no completely outdoor crops, because if the plant is placed in a room and the necessary conditions are created, then they will gradually acclimatize and will grow no worse than outside.
- Selecting a container for soil preparation. The bonsai technique involves the use of light soils with good drainage capacity. Stagnation of water should not be allowed, so you need to equip the container with high-quality drainage. Containers are selected from a wide variety, but to create creative compositions they often take containers of different geometric shapes. The main thing is that they are not deep - this will allow for proper development. In this case, you need to ensure that the color of the container is in harmony with the color of the plant itself.
- Watering. Based on the fact that the size of the container is quite limited, certain methods for irrigating such plants have been developed. This is either direct watering or placing the bonsai pot in a container of water. The frequency of irrigation depends on the chosen crop: some plants can easily tolerate periods of drought, while others require constant moisture. If you do not take into account the preferences of the bonsai, the root system may be damaged, which will lead to death. It is better to water miniature trees with rainwater, but tap water will also work if it is cleaned and allowed to settle. The temperature of the irrigation water should be close to the air temperature.
- Plants also need spraying to maintain the required level of humidity. Such events are held several times a day in the summer. The procedures allow the plant not only to freshen up, but also wash away dust particles from the leaves.
- Bonsai should be fed once every 7-10 days. To do this, use any garden fertilizers: urea, sapropel and others. algae-based fertilizing is also applied, but half as often. Fertilizers provide nutrition and strengthen the crop by replenishing nutrients in the soil. Fertilizers are applied in the form of powders, granules or solution.
But when feeding, you should adhere to several basic rules:
- at the initial stages of development, fertilizers with a low nitrogen content are used - they significantly accelerate growth
- a high concentration of nitrogen is acceptable when the leaves have become stronger, when the first wave of growth has subsided
- in spring and autumn it is customary to use complex balanced fertilizers. Plants with dormant periods stop feeding before the onset of cold weather
You should avoid feeding if the bonsai is sick, weakened or just transplanted.
Crown formation rules
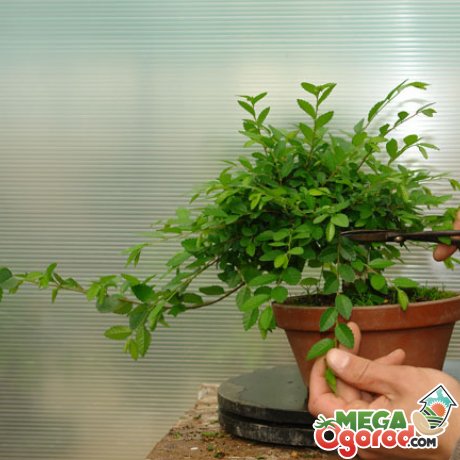

To reduce the size of a plant, you can use various methods:
- Seasonal pruning, which is the key to success when growing, but it must be done correctly, otherwise the plant will die.
- Direction of growth of branches and trunk using copper or aluminum wire.
- Creating the illusion of an old tree. To do this, remove the bark from the trunk of a living tree. But this must be done extremely carefully so as not to destroy the plant.
It is the main method of crown formation. It allows you to reduce the size of the tree, shape the location of the main branches, and also stimulate the growth of young shoots. But during such events, the bonsai experiences great stress, so manipulations can only be carried out on healthy and strong specimens.
Several types of pruning are used when forming bonsai:
- shaping, when large branches are cut out and the trunk is truncated, creating the shape of the future plant
- shortening branches, which allows you to increase volume and give a neat look
- light cutting of young shoots
- pinching to limit growth
- pruning of roots - for the growth of new root mass
Moreover, pruning of roots and crowns should be proportional and balanced.

Interest in the bonsai technique prompted gardeners and breeders to conduct a series of experiments, thanks to which the style of this method of growing plants was formed. Today there are quite a few styles of bonsai, including:
- "Chokkan" is presented in a classic upright style with simple and clear lines. This is the style that beginners prefer.
- "Shakkan" - expressed in a leaning tree.
- "Sokkan" has a forked trunk.
- "Moegi" has a unique barrel irregular shape, but the top of the crown is directed vertically.
- "Fukinagashi" looks like a tree bent in half, the trunk of which is parallel to the ground.
- Group plantings that depict a miniature grove.
- "Kengai" growing in a cascade.
Also used are styles of trees growing in stone or with a bare root system. But before you choose a specific style, you should check with experienced flower growers nuances of their formation and cultivation. Only after consultation it will become clear how difficult it is to grow such beauty.
Bonsai is not only beautiful miniatures, it is a corner of wildlife in a confined space (room or house).
The presence of such a living corner can always fill the soul with joy and good mood, calm a shaken nervous system and minimize discord in the family. The presence of bonsai reminds us that man is a piece of pristine nature, which modern people have long been forgotten, being in a constant pursuit of technical progress.
More information can be found in the video:
Bonsai is the art of recreating miniatures of real trees forced to grow in certain conditions. Depending on these hypothetical conditions, there are many types and styles of growing bonsai.
Bonsai styles
It must be said that this activity is quite exciting, especially since the resulting result is amazing and inspiring. Here are the classic types of bonsai with names and their explanations, so that you can choose and create your own bonsai.
Tekkan style(correct upright) is the first form of bonsai for beginners. It is characterized by a straight and cone-shaped trunk, thick roots, and the lower part of the trunk free from branches. The branches gradually become smaller towards the top. Almost any plant can be grown in this style. Symbolizes proud loneliness and unbending will.

Moyogi(irregular upright) - differs from the correct one by a curved trunk. Several bends may be present. The roots are visible on the surface, the crown does not extend beyond the bowl. You can grow juniper, pine, maple or oak in this style.

Fukinagashi(trunk in the wind) - repeats the shape of trees growing on the seashore, where the wind always has one direction and the branches are inclined in one direction. Birch and pine are best suited for this style.

Shakan (inclined trunk)– often found in bonsai collections. The plant grows with a thick or thin, but always inclined trunk; there are branches on both sides. For a more realistic picture of an inverted tree, some of the roots should be visible from the outside. In this way you can grow oak, linden, maple, thuja, pine and many other plants.

Ikada (raft)– bonsai in this style are rare. They are formed from a one-sided growing tree with a horizontally located and rooted trunk. The branches of such a tree are arranged vertically and look like many trunks. Suitable plant varieties are ficus, euonymus and some types of juniper.

Bonsai culture first became known in Japan and China more than two thousand years ago. Translated from Chinese, the word means “tree in a bowl.” Today, bonsai are widespread all over the world, but it is Japanese species distinguished by their elegance.
What does a bonsai tree mean?
Many people consider bonsai to be an ordinary tree, but this is not at all true. A real bonsai is a creation, a work of art that requires a lot of work. In the interior and exterior of the East, such a plant is a mandatory element.
Nothing can decorate landscape design just like bonsai. A photo of this beautiful plant is the best proof of its uniqueness. Modern bonsai is a whole symbolic system. With its help, you can bring many elements into reality: sea coast plants, alpine trees, meadow plants.
Under natural conditions, a tree acquires its appearance using the action of wind, sun, terrain. At home, bonsai formation is done manually- using wire, pruning shears and a knife.
In the homeland of bonsai, it is believed that the older the plant, the more noble it is. Vintage compositions decorate best places East. The scale of a bonsai in relation to an ordinary tree, of which it is a copy, is 1:100.
How to make your own bonsai?
The process of creating bonsai on your own is quite labor-intensive, lengthy and complex, but very interesting. Before you figure out how to grow a bonsai, you should study the main stages of growing a plant. Conventionally, they can be divided into eight successive steps:
- selection of the original tree blank for bonsai;
- tree top trimming;
- periodic pruning of branches and root system with concave pruning shears;
- formation of a bonsai crown from buds;
- forming branches for the bonsai crown, trimming excess branches;
- shaping branches using wire;
- shortening young shoots for better branching and compactness of the bonsai;
- replanting a bonsai into a miniature pot and creating a composition.
Basic requirements for traditional bonsai
A real home bonsai must meet a number of characteristics:
- powerful trunk with strong roots;
- clear line of branches;
- branches and trunk - the foundation of the plant, which should be visible through the leaves;
- visual similarity to the original tree;
- bowl for planting - simple, dim design;
- design matching of pot and plant.
Bonsai trees differ from each other in two main characteristics:
- size;
- form.
There are two ways to form a plant:
- using wire;
- without using wire.
The technique of forming a crown using wire appeared not so long ago, but has become quite firmly established. With its help you can create a wide variety of unique crown shapes.
Instead of wire, you can also use pins with rubber gaskets or weights to form a bonsai.
The following types of bonsai trees are distinguished by size: large (up to 1 m 20 cm); medium (up to 60 cm); small (up to 30 cm); miniature (up to 15 cm). As a rule, bonsai at home is a miniature plant that evokes a state of awe, incredible beauty and the fragility of a young girl.
Growing Bonsai large sizes practically no different from miniature subspecies. There are only a few special creation conditions:
- formation of a low base (up to three branches);
- planting in a large bowl to form a thickened trunk;
- increased watering;
- annual replanting with removal of unnecessary roots;
- non-concentrated fertilizers.
The most common forms of bonsai: vertical symmetrical, vertical asymmetrical, inclined, bent, cascading, rocky, forked, three-trunked, multi-trunked.
On the pedestal of the most whimsical indoor plants can safely be classified as a banzai tree. Caring for this plant at home is a rather labor-intensive and difficult process. 
Failure to follow the rules for maintaining a bonsai can cause its death. Therefore, if the slightest doubt arises about the possibility of providing the necessary conditions, it is better to initially abandon the idea of \u200b\u200bgrowing bonsai. For favorable growth of bonsai, you should create optimal conditions for it:
- light mode;
- air humidity;
- temperature regime;
- priming;
- watering;
- fertilizer.
Bonsai is a light-loving plant that does not have enough natural light, so you will have to take care of a source of additional lighting. Otherwise, the plant will begin to experience light deficiency. The greatest need for abundant lighting is in winter.
The main parameters that you should pay attention to when choosing a place for a bonsai are the side of lighting, the angle of incidence of the sun's rays, and the color of the walls.
The best source of additional lighting is a fluorescent lamp, which has a high coefficient useful action and is easy to use. The closer the lamp is to the plant, the greater the effect of its presence., but at the same time, do not forget about the power of thermal radiation, which can be harmful. The optimal location of the lamp is 30-40 cm from the plant.
The optimal temperature for keeping a bonsai depends on what type of plant it belongs to:
- for subtropical subspecies, the temperature in winter fluctuates in the range of 5-15 degrees, in the warm period it can be kept in the open air;
- for tropical subspecies the required temperature is 20-25 degrees.
Do not forget that there is a directly proportional relationship between the temperature and the amount of watering: the higher the temperature, the more often the plant needs watering.
There is not enough moisture in a standard room to create favorable conditions for bonsai, so it needs additional air humidification. To do this, you can spray the leaves with water daily or purchase an electric humidifier. The second option is more convenient, but quite expensive. 
The soil in the bonsai bowl should be constantly moist, it should not be allowed to dry out, as this will damage the root system and the plant as a whole. The soil dryness level is determined manually. Be sure to completely wet the ground before water flows out of the drains. In the warm season, bonsai needs more frequent watering than in winter. The most suitable water for irrigation is boiled and melted water.
It is best to plant bonsai in special soil, which is sold in specialized stores. Soil for indoor plants is not suitable for bonsai, as it has an unsuitable composition for it.
The fertilizer can be either a universal (for most plants) or a special (exclusively for bonsai) substance.












