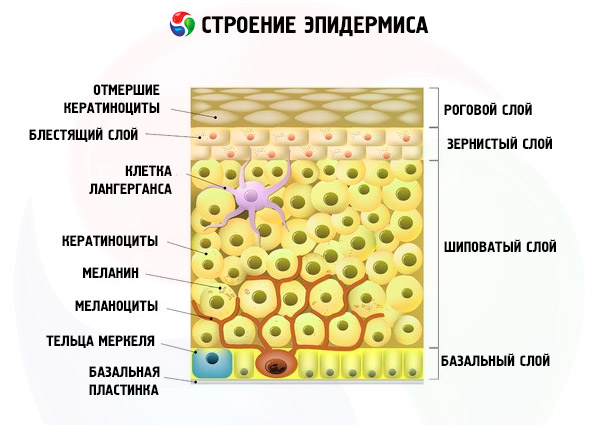
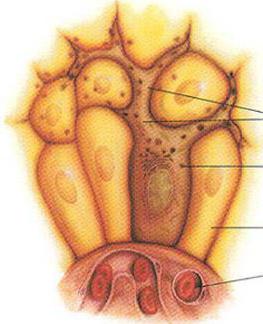
It is generally accepted that the causes of the appearance of moles on the body, which can form in any part of it, lie in the benign local proliferation of melanocytes - dendritic cells of the basal layer of the epidermis.
These are the only cells that synthesize the pigment melanin, which protects the skin from ultraviolet rays and determines the color of the skin, hair and eyes.
By structure and properties, melanin is a UV-filtering biopolymer, which is obtained in the course of a multi-stage biochemical transformation of tyrosine α-amino acid; the pigment is deposited in melanocyte organelles - melanosomes, and enters the upper layers of our skin thanks to keratinocytes.
Accumulating in one place, melanocytes form moles, and their average number in one person is from 30 to 40.
Key causes of moles in adults and children
For clarification true reason the appearance of moles by biologists and physicians have been and are being (and will be) numerous biochemical and genetic studies.
At the same time, experts remind that the skin is the most important multifunctional organ, the laying of which occurs in the process of embryogenesis, that is, during the development of the human embryo.
Most moles appear during the first 20 to 30 years of a person's life and, according to statistics, only one out of every 100 babies has a mole at the time of birth. And the reasons for the appearance of moles in a child, that is, congenital nevi (in Latin, naevus means " birthmark”) is associated with a minor malformation of embryonic development in the first twelve weeks of pregnancy.
Skin pigment-producing melanocytes are formed from the neural crest cells of melanoblasts, which initial stages embryogenesis are dispersed along the upper (dorsal) part of the neural crest in various parts of the body (squamous epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes, hair follicles, tissues of the arachnoid membrane of the brain). In the basal layer of the epidermis, melanoblasts mature into melanocytes capable of producing melanin. The defect is believed to result in accelerated melanocyte proliferation.
This means that their excess is formed, and "excessive" melanocytes do not spread evenly in the skin, but gather together - in nests, clusters, islets - in the very top layer skin and even protrude from it.
Recent research clears things up a bit. The fact is that some melanocytes arise from melanoblasts migrating ventrally - along the lower surface of the neural tube, and then along the nerves. These melanocyte precursor cells give rise to the peripheral nervous system and adrenal medulla. Thus, they find themselves in the sheaths of nerves and axons, among Schwann cells, and are able to produce melanocytes after birth.
There is scientific evidence that melanocytes in moles are modified into so-called dermal nevus cells - skin nevus cells. This variant of melanocytes differs from the usual one in its size, volume of the cytoplasm and the absence of processes (dendrites). They are usually located at the junction of dermis to epithelial tissue, and depending on the degree of maturity, they can be further classified as epithelioid, lymphocytoid, and neuroid. It is claimed that nevus cells are able to migrate, penetrating into the lymph nodes and even into the thymus gland (thymus), where immunocompetent cells - lymphocytes - are formed and mature.
To date, it has been established that in 60% of cases the causes of the appearance of moles in adults and children are hereditary. More than 125 different genes are already known to regulate pigmentation, either directly or indirectly. Many of these genes control the differentiation of melanocytes or affect the biogenesis and function of melanosomes, and also provide participation in the biochemical processes of pigmentation and proliferation of epithelial cells of hormones, growth factors, transmembrane receptors (EphR, EDNRB2, etc.), transcription factors (such as MITF, Sox10, Pax3, etc.). The interaction of the totality of all of the above determines the causes of the appearance of new moles.
Speaking of hormones. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and in patients diabetes often contribute to the formation of moles. And the hormonal causes of the appearance of moles in a child and adolescent are explained, first of all, by the activity of hormones and biochemical growth factors (for example, SCF stem cell factor): after all, children grow, and the area of the skin is constantly increasing. Also, in a growing body, melanocortins produced by the pituitary gland are very active - hormones that purposefully stimulate the synthesis of melanin (they also affect the production of corticosteroids in the adrenal cortex and the activity of lipid metabolism in adipose tissue cells).
Under the influence of solar radiation, melanin synthesis increases (and we see this when a tan appears). All this is the result of the activation of tyrosinase in melanocytes, which provides increased protection of the skin from UV. Some scientists suggest that excessive sun exposure may play a role in the formation of acquired moles. So far, the biomechanics of the interaction between genetic structure and overall exposure to ultraviolet rays has not been elucidated. However, in favor of the fact that this is exactly the case, the almost complete absence of moles on the buttocks testifies ...
Causes of moles on the neck, face and armpits
Almost everyone is interested in answers to three questions:
- Are there any special reasons for the appearance of moles on the face?
- What are the causes of moles on the neck?
- What are the reasons for the appearance of a mole under the armpits - in such an uncomfortable place, which, in general, is not exposed to the sun?
We will try to answer them, based on what is already known to clinical dermatology regarding the formation of epidermal nevi of the indicated localization.
Melanocytes are located between basal keratinocytes in an approximate ratio of one to ten and distribute melanin through their elongated processes (dendrites), as well as through direct cell contacts. As you know, keratin skin cells in the upper layers of the epidermis replace each other quite quickly and, rising up (to the stratum corneum of the skin), carry away the captured melanin - to form a barrier against ultraviolet rays.
At the same time, in different parts of the epidermis, the content of melanin and the number of cells producing it are different: in the skin of the head (including the face), as well as the neck and hands, there are twice as many melanocytes as in other parts of our body. Obviously, this is due to the fact that these areas are much more open, and they get the most sunlight.
Among the not yet proven versions of the cause of the appearance of moles on the face, there is an assumption that the process of formation of nevus skin cells is promoted by increased metabolism in the cells of the epidermis - due to the stressful effects of changes in temperature and air humidity on the skin of the face, as well as constant stretching-compression of the skin by facial facial muscles .
In addition, there is an opinion that there may be reasons for the appearance of moles on the neck associated with impaired formation and distribution of melanin in areas of the epidermis directly above the nerves of the cervical plexus (see above - about the migration of melanoblasts during embryo development). These are the branches of the motor, cutaneous and phrenic nerves, which are connected by loops and are located on the neck (behind, in front and on both sides).
But researchers tend to see the reasons for the appearance of a mole under the armpits in the presence of hair follicles and glands in the skin of the armpits - sweat and apocrine. But the specific mechanism for the formation of nevi in the armpits has not yet been studied. Moreover, it remains unknown how the flow of melanocytes into the epidermis is controlled, although, of course, there is a regulatory scheme for this process.
Causes of pink and red moles
Most probable cause the appearance of red moles lies in the fact that the "body" of the nevus can be not only melanocytes, but also cells of the epidermal connective tissue, accessory fibers, and vascular elements. The so-called vascular nevi (nevus vascularis) are manifested by reddish swellings or spots of various sizes on the skin due to capillary hypertrophy - the growth of blood vessels in the skin.
In addition, there may be a connection with a lack of blood clotting factors and vitamin K, which leads to increased bleeding when the walls of skin capillaries that are partially trapped in the formation are damaged.
According to dermatologists, red moles are typical for diagnoses such as autoimmune rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus.
The causes of the appearance of red convex moles are similar. At the same time, their "bulge" (as in the case of brown moles) is the result of the fact that melanocytes are often located significantly above the dermoepidermal junction and are localized in the upper layer of the epidermis, including the granular zone and the stratum corneum.
The reasons for the appearance of pink and red moles do not exclude the influence of the composition of the melanin produced. Melanin can be either brown-black (eumelanin) or reddish-orange (pheomelanin). In the latter case - especially in red-haired and natural blondes- moles are often light beige or pink.
Reasons for the appearance of hanging moles
It is unnecessary to say that the cause of the appearance of a mole on the leg, as well as the causes of the appearance of hanging moles on the neck, have been thoroughly studied. Although much attention is paid to the study of the etiology of this variety of epidermal nevi.
Thus, an association of a melanocytic nevus with eccrine sweat glands was revealed, which is expressed not only in the capture of the body of the mole of the gland itself (which may be located in the center of the mole), but also in the exit of nevus cells in the form of a node to the outside - through the eccrine ducts.
In other cases, the feature of infiltration leads to a linear pattern of distribution of intradermal nevus cells. Going beyond the dermo-epidermal border and the papillary layer of the skin, a group of such cells penetrates the surface, expanding part of the epidermis between the collagen fibers. Moreover, intradermal nevus cells can form a pigmented dome-shaped or papillomatous papule (up to 1 cm in diameter) with a stalk. A mollusk-shaped form with a broad base is also possible, with a color ranging from light brown and black to whitish or pink-red.
Hanging moles can form anywhere, but their “favorite places” are the neck area, armpits and skin in the perineal area.
In the middle of the last decade, researchers at King's College London examined 1,200 non-identical female twins aged 18 to 79 and found that those who had more moles on their bodies also had stronger bones, i.e. they are less likely to develop osteoporosis. In addition, in older women with more than 60 moles, the skin was less wrinkled, and they looked younger than their years ... It turned out that in people with a large number of moles, the chromosomes have unusually long telomeres - the terminal sections of DNA polymerase, which prolongs the period of active replication and postpones many age-related processes in the body.
And dermatologists advise - regardless of the time and cause of the appearance of moles - for any changes in epidermal nevi, contact specialists, since the risk of developing skin cancer associated with the presence of moles is quite high.
It is impossible to imagine a person who does not have a single mole on his body. They appear on the skin of people of all races - white, black, red, yellow. But for some, such spots can be easily counted, they may turn out to be no more than 40, while others have a huge number. Why do new moles appear? And anyway, what kind of education?
Young parents, when they see their long-awaited child, are usually discouraged: there are absolutely no moles on his body. So it is - the first moles, or scientifically nevi (from the Latin words naevus maternus), begin to appear only after a few months.
Do not confuse moles with birthmarks - those are present on the skin from the first minutes of life. The reasons for the formation of moles are not exactly and unequivocally established. But most experts who are engaged in research of this phenomenon distinguish several circumstances. Here, in their opinion, are the main reasons why new moles appear on the body ...
Heredity
It has long been noticed: very often moles appear on the skin of children in the same place where one of the parents has them. This is sometimes seen from generation to generation. Today, this is explained by the predisposition of skin cells to mutations, which is already laid down at the level of human DNA.
Hormonal surge
The appearance of new moles is observed during puberty of adolescents. A huge amount of hormones released into the body cause a concentration of melanin in melanocyte cells. They are located both in the upper layer of the skin - the epidermis, and in the deeper - the dermis.
The same happens in pregnant women, and moles can both appear and disappear. Some take care of this in advance, aligning their hormonal background. If preventive measures are taken, new nevi will not appear.
ultraviolet irradiation
Under this name, ordinary sunlight is hidden. Under the direct influence of the sun's rays, all skin cells, including melanocytes, are activated, after which the number of moles increases. Some fans of bronze tanning in a solarium are also surprised to find that there are more moles on their skin than before the procedure.
Infection and injury
Any damage to the upper layer of the skin, especially if it does not heal for a long time, can become a trigger for the formation of new formations. Some experts argue that the bites of harmless insects - mosquitoes, bees and others - are not at all so safe. Particular attention should be paid to preventing infection, such as papilloma, from penetrating the skin.
The nevi themselves are benign formations. And if new moles appear on the skin, this is a completely natural life process, which is why you should not sound the alarm.
Some Western scientists, primarily the British, have recently been actively putting forward the version that the presence of a large number moles indicate a long lifespan. Such hypotheses have not yet been absolutely confirmed by anyone. But if some new moles have appeared, their possible degeneration into a cancerous tumor has been proven and, according to statistics, is almost 50% of the number of diseases.
Types of nevi
If new moles began to appear on different parts of the skin in those areas where they had never been before, you should not panic. First you need to determine the type of neoplasm and the likelihood of its degeneration into a cancerous tumor. For this, a simple visual inspection by a specialist is quite enough. In modern medicine, moles are classified into a number of types.
Lentigo
They can be found anywhere on the body, including mucous membranes. Development occurs in the dermis, they do not rise above the surface of the skin, they are usually brown in color, almost dark. The appearance of such formations is in no way connected with solar radiation: they practically do not react to it.
Epidermal-dermal
Why many new moles appear most often on the feet, hands, and genitals is still unknown. Coloring has a wide range - from yellow to black. They protrude just a little above the skin.
Moles are complex
The appearance of such formations occurs if melanocyte cells are located in the epidermis and in the dermis. Visibly protrude above the skin, usually a dark brown hue.
Intradermal nevi
Convex, distinguished by a wide range of colors - from flesh tone to black. A distinctive feature: a lot of hairs can grow around such moles and on their surface.
Nevuses of Sotton
 The causes and appearance of new moles of this species remain and, probably, will remain a mystery to specialists for a long time to come. The fact is that these formations appear and disappear without any patterns and reasons. Their main difference is White spot directly around the nevus. One thing reassures - according to the observations of researchers, moles of this type almost never degenerate into melanoma - skin cancer.
The causes and appearance of new moles of this species remain and, probably, will remain a mystery to specialists for a long time to come. The fact is that these formations appear and disappear without any patterns and reasons. Their main difference is White spot directly around the nevus. One thing reassures - according to the observations of researchers, moles of this type almost never degenerate into melanoma - skin cancer.
Moles are dysplastic
Reddish tint, with fuzzy blurred borders, usually localized on the chest, back and buttocks. The appearance of such nevi depends entirely on the genetic predisposition.
Blue nevi
These are smooth, protruding hemispheres above the skin of the formation of all shades of blue color. May appear on the buttocks, limbs, face.
Giant pigmented nevi
This is an innate phenomenon. They give the owners a lot of trouble because they increase in size simultaneously with the growth of a person. They can be on the neck, face, which creates a feeling of severe discomfort. The particular danger of such congenital formations is that more than 50% of them are eventually modified into cancerous tumors.
Why new moles appear on the skin: Video
Vascular moles
All of the above types of moles are non-vascular formations. But what if there are more moles of a reddish, purple, bluish color? Such nevi are called hemangiomas, the causes are in the anomalies in the development of blood vessels, which is why such an unusual color appears.
The formation of these nevi depends largely on prenatal development circulatory system or previous diseases. But usually hemangiomas are congenital, babies are born already with them. Require constant supervision. If the mole becomes larger, negatively affects the skin and neighboring organs, then it is necessary to excise and remove it.
Why moles appear: Video
Remove or not remove a new mole
Many people roughly know: if new moles appear, it means that there are Great chance their transformation into malignant tumors. This is especially true for those women who have light thin skin or a genetic predisposition to neoplasms.
The question arises: is it worth removing such a mole? Only a dermatologist-oncologist can answer it after a thorough examination and complex necessary analyzes. But, having such neoplasms on the skin, you need to always be on your guard even without doctors. In what cases should you sound the alarm?
Location of moles
- Moles are located in open areas of the body, that is, they are always at risk of injury.
- Nevi are constantly rubbed with clothes or shoes, often damaged (for example, when shaving).
Shape change
- Rapid growth of a previously invisible mole.
- New formations begin to change the structure - the surface becomes harder or softer, tubercles appear on the surface, etc.
Color, pain, discharge
- Suddenly, painful sensations appeared both in the mole itself and around it, even with a slight stroking.
- Any unexpected discoloration of a nevus.
- or red halo.
- or fluid is released.
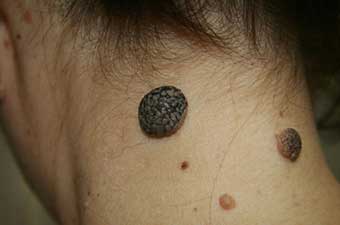 If any of these signs appear, this is a danger signal! But never jump to conclusions. Never attempt on your own or use any "proven folk remedies"! Remember - no "grandmother's advice" will help here, but they can do harm, and very much.
If any of these signs appear, this is a danger signal! But never jump to conclusions. Never attempt on your own or use any "proven folk remedies"! Remember - no "grandmother's advice" will help here, but they can do harm, and very much.
Beware also of removing new moles from a clean cosmetic purpose. Remember that there are no databases of extremely necessary indications that threaten your health and life! And only a qualified specialist can determine this.
Take care of your health, and you will always be beautiful, cheerful and healthy!
How to remove moles from the face: Video
Have you ever tried to get rid of papillomas, moles and warts? Judging by the fact that you are reading these lines, the victory was not on your side.
And have you already thought about laser removal or other procedures? It is understandable, because it is discomfort, a minus for your appearance and the risk of developing oncology.
But perhaps it is more correct to remove not the consequence, but the cause? Read about the special issue of Elena Malysheva and find out how to get rid of neoplasms forever!
Formations on the skin in the form of small spots are popularly called moles. Most often they are dark brown in color and small in size. In some cases there are exceptions. There may be large and raised moles above the skin. Also, their color is red, black, light brown. The name of such formations is due to the fact that they appear at birth. However, this is not always the case. Unlike birthmarks, these elements appear on the skin at any age. Their appearance is influenced by endo- and exogenous factors.
Moles on the body: varieties
Many people over the years notice the appearance of moles on the body. The reasons for their spread are not always clear, since such formations are rarely a cause for concern. However, moles are worth paying attention to. In some cases, they may indicate the threat of developing a skin tumor. There are the following types of moles:
- Brown formations on the body. Relate to age spots. They are brown in color because they are formed by melanocytes. Often these benign formations do not rise above the surface of the skin and occur in childhood.
- Red moles on the body. The causes of these spots are associated with the expansion of small vessels of the skin. Another name for these formations is hemangiomas. They are various shapes and size. Often, red moles are on the body already at the birth of a child. They rarely appear in adults.
- Towering above the surface of the skin (hanging) moles on the body. The reasons for the appearance of such formations are the accumulation of pigment-producing cells in the deep layers of the skin. Often they are localized on the neck, in the armpits and inguinal region.
- Large moles on the body. Able to develop both due to the accumulation of pigment, and due to vascular changes. Such formations are called birthmarks. These items take up a lot of space. skin and have different shapes. Frequent localization of such spots is the back, face, limbs.
- Blue moles on the body. The causes of these spots are the accumulation of melanocytes in the deep layers of the skin. blue tint nevi due to the optical effect. Such moles are dangerous formations, as they can develop into a tumor.
Any formations that have arisen on the body must be shown to the doctor. After all, some of them must be removed, others do not pose a health hazard.

Causes of brown moles on the skin
Why do moles appear on the body? The causes of these formations may be different. The mechanisms of accumulation of melanin in the layers of the skin include factors due to genetic characteristics (congenital), endo- and exogenous changes. Due to the redistribution of the pigment, moles appear on the body. The reasons for their formation are as follows:
- Heredity. The genetic theory of the occurrence of moles has not been scientifically confirmed. However, it is noted that large dark spots on the body are often inherited. Also, the frequency of their occurrence increases in persons of the Mongoloid race.
- Ultraviolet irradiation. It is believed that people who stay in the sun for a long time, moles appear more often. This is due to the excessive formation of melanin and its redistribution over the skin.
- Production of hormones by the pituitary gland. Some biologically active substances secreted by the endocrine glands contribute to the production of melanin. Therefore, increased pigmentation often occurs during puberty, during pregnancy, menopause.
- Metabolic disorders in the body. Improper distribution and excess of melanin occur in diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
- Radiation exposure. Stimulates the production of pigment - melanin.
- Excess dietary intake of copper. This chemical element is found in meat and seafood. Also, the production of melanin stimulates the use of beans, dates, milk, fish.
In addition to the above reasons, exogenous factors include mechanical damage to the skin and the penetration of viral particles.
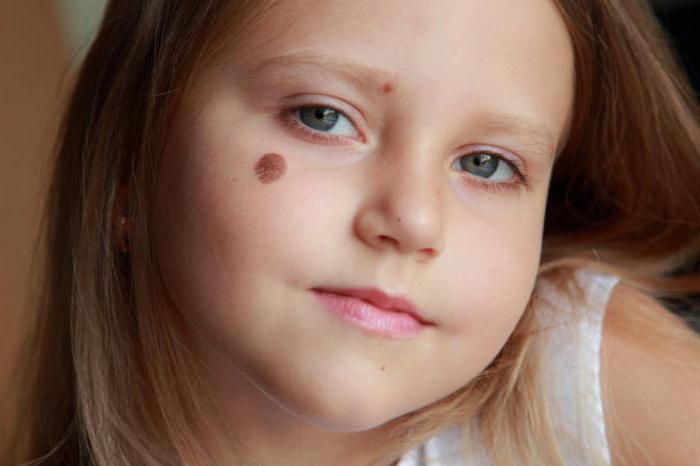
The appearance of moles in women
Due to the fact that the fairer sex is more likely to pay attention to the condition of their skin and visit the clinic and beauty salons, it is believed that moles on the body are more common among them. The reasons for the appearance of brown or red spots in women can be different. Often these are hormonal changes in the body. Among women, acquired moles are common, that is, spots that appear in an adult or adolescence.
Doctors attribute this fact to the constant hormonal changes observed in the body of the weaker sex. Moles that appear in women are rarely permanent and may disappear on their own. Age spots occur during pregnancy, as well as in the postpartum period. Increased production of melanin affects the staining of the midline of the abdomen, nipples. If there is too much pigment, then its accumulations are formed in various parts of the body - moles.
Another cause of brown spots is HPV (human papillomavirus). Some types of this pathogen lead to the formation of nevi on the skin.
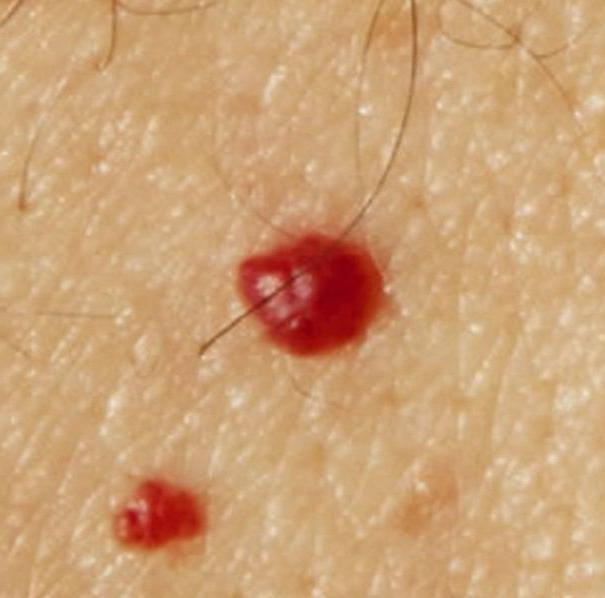
Moles in men: causes
Among the representatives of the stronger sex, moles on the body are less common. The reasons for the appearance in men are the same as in women. However, hormonal factors are not so pronounced. Often, moles appear in men at birth and in childhood. Brown age spots can occur due to metabolic and endocrine diseases. Another factor is frequent exposure to the sun. Unlike the female population, adult men are more likely to have red moles on their bodies. The causes of hemangiomas are excessive physical activity, malnutrition and chronic diseases. Among them are pathologies of the digestive and cardiovascular systems.
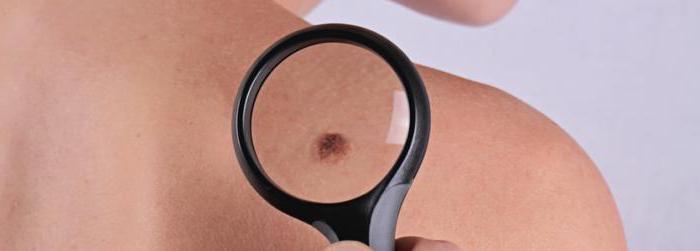
What is the peculiarity of red moles?
Why do new moles appear on the body? The reasons for the appearance, photos of these benign formations are contained in various medical sources. However, only a doctor can establish a connection between provoking endo- and exogenous factors and the occurrence of moles. Unlike brown pigment spots formed by the accumulation of melanocytes, red elements are composed of vascular tissue. Hemangiomas are benign tumors. They may vary in size and shape. Red moles are formed by blood vessels - small superficial veins, arteries and capillaries. Their feature is that hemangiomas turn pale when pressed. Like brown moles, red spots are flat and protruding from the surface of the skin. Congenital hemangiomas may disappear on their own in childhood.
The influence of exogenous factors on the development of moles
Due to exogenous factors, moles appear on the body. The reasons for the formation of these skin elements are ultraviolet and radiation radiation, injuries of the integumentary epithelium. Thus, brown moles are formed. Under the influence of sunlight, melanin is produced in the body in greater quantities. Excessive ultraviolet radiation leads to improper distribution of the pigment. Because of this, foci of its accumulation are formed - moles. Radiation has the same effect.
Injuries to the skin lead to scratches, which are the entry gate for viruses. Due to the ingress of microorganisms, infection occurs. Some viruses cause the appearance of benign formations on the skin - moles, warts and papillomas. To avoid this, it is necessary to treat wounds with disinfectant solutions.
Reasons for the danger of moles
The danger of moles lies in the possibility of attachment bacterial infection and malignancy. Most often, microbes penetrate when large (hanging) benign formations are injured, which are subjected to friction against clothing. It is necessary to contact a dermatologist or oncologist in cases where there is:
- Change in color or size of a mole.
- Appearance discomfort in the field of good quality education.
- Itching at the site of the mole.
- The appearance of a red rim around the spot.
- The appearance of blue nevi on the skin.
All these changes may indicate malignancy, that is, transformation into a cancerous tumor (melanoma).
Red moles on the body: causes, photos of formations
The factors influencing the occurrence of hemangiomas are vascular diseases and digestive system. Often, with chronic pancreatitis, red moles form on the body. The reasons for the appearance, photos of hemangiomas can be found in this article. Red moles rarely undergo malignant transformation. Large vascular formations can bleed with injuries.
Moles on the body: causes of appearance, removal of spots
In most cases, benign formations are subject only to observation. The exceptions are hanging and large, as well as dangerous moles on the body. The causes of the appearance, the removal of these elements by surgery (the need for treatment) can only be determined by an oncologist. If the doctor determines that the formation does not consist of malignant cells, then you can get rid of it. If the cause of the appearance of a brown or red spot is identified, the doctor makes recommendations and prescribes medication.
Methods for removing moles on the body
Methods for removing moles include surgical and laser treatment. The surgical procedure should be carried out after a doctor's examination and a cytological examination. Laser removal is possible if the mole is small and does not belong to dangerous types of benign tumors.
A nevus, or mole, is a benign formation that appears from birth or is formed during life. They can be different in shape, color and size. Some neoplasms are considered potentially dangerous, others are a highlight of appearance and do not cause any trouble. Often the appearance of nevi indicates the development of disorders in the body. Possible reasons the development of pathology can be identified by a qualified specialist.
congenital moles
The appearance of moles on the body is a consequence of the accumulation of pigment skin cells. In fact, a congenital mole is a defect in embryonic development. An interesting fact is that nevi may not be noticeable on the body of a newborn child. Moles grow most often in the second year of life. Small neoplasms are not dangerous in terms of degeneration into a malignant tumor. Often such nevi do not cause trouble to a person and are only a feature of appearance.
Hemangiomas deserve special attention. These are large red spots, with which in most cases the child is already born. Such formations rarely degenerate into a malignant tumor. But they can rapidly increase in size with age, affecting neighboring organs and tissues.
Often, hemangiomas on the face of a child are the cause of hearing and vision impairment. In addition, a large red spot is a cosmetic defect. Hemangiomas cannot disappear on their own. The sooner the defect is removed, the less likely it is to develop complications.
The exact causes of congenital red spots are not known today. However, most doctors agree that the defect is associated with disorders in the mother's body during pregnancy. If a woman has had the flu or a bacterial disease, the risk of developing a hemangioma in an infant increases. Statistical data indicate that they are more common in families living in regions with a poor environmental situation. Girls are twice as likely to be born with a hemangioma than boys.
Hemangioma - a congenital malformation on the skin of a child
Congenital birthmarks (pigmented) spots do not pose a health hazard and do not require special therapy. Often the appearance of such a mole in a certain area of \u200b\u200bthe body is genetically determined. Hormonal disorders in the mother's body are also often the cause of age spots on the baby's body.
Why do moles appear during life?
The appearance of new moles on the body may be due to various factors. In most cases, a large number of nevi begin to appear during adolescence. This is explained quite simply. The fact is that the failure of the formation of melanin skin pigment occurs due to hormonal changes in the body. For the same reason, moles on the body grow in women during pregnancy or the previously formed ones disappear. The described hormonal changes are the norm and do not require medical intervention.
The number of moles changes throughout life
If moles appear and it is impossible to explain the cause of this condition, you should seek help from a specialist. Often a large number of nevi is observed in women who are being treated for infertility. Men face the problem much less often.
The disposing factor in the formation of new marks on the body are ultra-violet rays. It is the sun that activates the production of melanin, as a result of which the body is covered with a tan. For this reason, moles appear most often in open areas - on the face, arms, shoulders in summer period. The situation worsens with age. Older bronze tan lovers may notice how after taking sunbathing the body is sprinkled with small nevi.
People who initially have a large number of spots on their bodies should avoid prolonged exposure to open ultraviolet rays.
It should be borne in mind that nevi may have a tendency to malignant degeneration. Unfortunately, it is impossible to predict how a particular mole will behave.
Where do moles appear on the body of a person who refuses to tan? There are other reasons why brown or burgundy nevi appear on the skin. The radiation background can contribute to the formation of neoplasms. It was noticed that the bodies of people who took part in the liquidation of the Chernobyl disaster were covered with brown spots. In many cases, such moles had a tendency to malignant degeneration. Many liquidators died in the 90s from skin cancer.
A large number of nevi on the body is a reason to consult an oncologist
Common are nevi, which appear due to injuries or damage to the epidermis by viruses. Hanging neoplasms, for example, are papillomas. The virus is often transmitted through sexual contact. For a long time, marks remain on the body after an insect bite. If a person has sensitive skin, bees often form at the site of a sting. dark spots which disappear only after a few months.
Adherents of Chinese medicine have their own opinion about the formation of new moles on the body. Experts believe that any mole is the result of a violation of body systems. Any disease leads to the accumulation of negative energy, as a result, marks appear.
Reasons for the disappearance of moles
If a nevus that has existed on the body since an early age has disappeared, there may also be cause for concern. How do moles disappear? In most cases, this process occurs gradually. Initially, a light halo appears around the nevus. Then the area without pigment captures the surface of the mole. Subsequently, a light spot remains at the site of the mole. In some cases, the area with the former mole becomes a normal skin color.
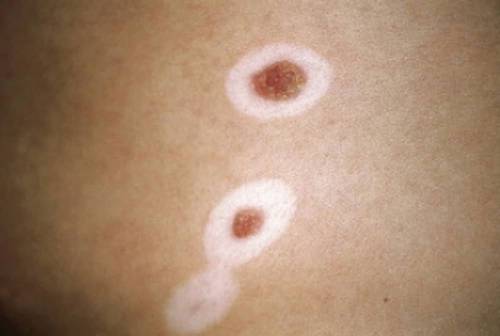
A light halo around the nevus is one of the signs of vitiligo
Why are nevi needed? Should I be worried if they disappear? In fact, moles do not have any function. But the disappearance of the neoplasm may indicate changes in the body. Depigmentation (disappearance of melanin) often indicates the development of vitiligo. This is a complex disease that is more often inherited. If moles disappear, you should seek help from a dermatologist, undergo a complete medical examination.
Lightening of the nevus may also indicate its degeneration into melanoma. This is a malignant tumor that requires immediate treatment. An unpleasant signal will also be an increase in the size of the neoplasm. Melanomas are usually larger than 5 mm in diameter.
When should you see a doctor?
If new nevi rapidly began to appear or existing formations begin to grow, you should not postpone a visit to an oncologist. If new moles appear, there is no reason to panic, but it is advisable to conduct a series of studies. Even neoplasms with a uniform color with a diameter of up to 6 mm are considered safe.
- behind a short time the shape and color of the mole has changed;
- bleeding appeared from the formation;
- in the area of the nevus, itching or burning is observed;
- pus flows out of the neoplasm.
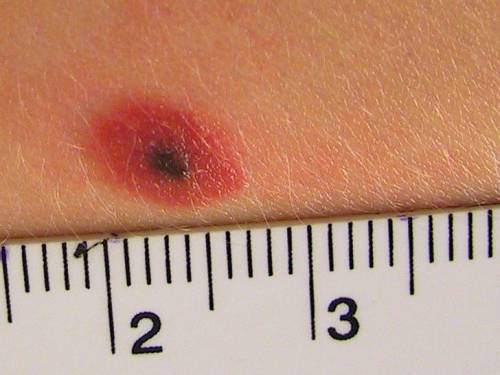
If the mole is inflamed, you can not postpone a visit to the doctor
The described symptoms may indicate a malignant degeneration of a mole or its inflammation. If a nevus causes psychological or physical discomfort to a person, the specialist will recommend removing it. A histological examination of the neoplasm will be preliminarily performed.
There are several ways to get rid of nevi. In most state medical institutions apply standard excision. After the operation, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, bacterial therapy is carried out as a prophylaxis. In private clinics, moles are removed using a laser. The advantage of such an operation is that after the intervention there is no scar on the body.
How to prevent the appearance of moles?
If a person has a tendency to a rapid increase in the number of nevi, it is impossible to postpone a visit to the doctor. The specialist will find out, as a result of which moles appear, how to protect the patient from the emergence of new formations. A mandatory measure for people with a large number of nevi is the rejection of direct ultraviolet radiation. You will have to give up sunburn, use special protective cosmetics. It is not advisable to go outside between 11:00 and 17:00.
Any moles or birthmarks should be treated with special attention. In no case should you scratch neoplasms, pull out the hairs growing in them.
Large nevus requires careful examination
Any mechanical impact can lead to inflammation of the nevus or its malignant degeneration. If moles appear on the body, which are subjected to constant mechanical stress (friction), such neoplasms should be removed.
How moles appear, where the neoplasm comes from - all these questions can only be answered by a specialist. Therefore, if the number of nevi is growing rapidly, you should make an appointment with a doctor in the near future.
Benign skin tumors or malformations of their development, which appeared due to a violation of the synthesis and metabolism of melanin, are called moles. They are different: flat, convex or, conversely, smooth, hairy. Moles do not cause inconvenience and are considered cosmetic defect. However, some nevi can easily degenerate from benign to malignant, which poses a threat to human life. Why do moles appear and how to deal with them?
Why do they appear
- Exposure to radiation. Ordinary sunlight can cause skin mutation, as it contains a large amount of ultraviolet radiation, which stimulates the formation of moles. This is especially noticeable in people with fair skin, their body does not absorb ultraviolet light well, as a result of which a skin mutation develops. Many experts believe that the appearance of new moles is associated with exposure to radiation or x-rays, because throughout life every person is exposed to radiation every year (for example, fluorography or x-rays).
- Injury to moles. Tight or narrow clothing, seams located in uncomfortable places, systematic rubbing with rough material injures an existing mole. The owner himself can injure it - accidentally cut it or pick it up. In this case, melanocytes are activated and appear on the surface of the skin with new formations.
- Viruses. They also play a big role viral infections such as viral papilloma. Its cells contain several genes that cause them to divide much more frequently. The result of growth is unpredictable: it can be either a common wart or malignant or benign formations.
- hereditary predisposition. Information embedded in DNA is often the cause of the appearance of hereditary moles. They are of the same shape and size as those of relatives, they are often even located in the same places, for example, on the face, neck, folds of the arms, fingers.
- Hormonal changes. One of the hormones produced by the pituitary gland has a strong effect on the release of melanin. So often, moles appear in adolescents during puberty, but under the influence of hormones, they can disappear on their own and disappear from the body. Therefore, during this period of life, moles do not carry an oncological danger, this is a normal reaction of the body to changes in the hormonal background.
Kinds
Moles are congenital - appear immediately at birth, and acquired - are formed throughout life. Most of all they appear during pregnancy, in adolescence and with menopause in women. Nevi can occur anywhere on the skin, in particular, on the mucous membranes.
Depending on the depth of the skin layer on which they appeared, they are divided into the following types:
- Borderline - appear at the border of the dermis and epidermis.
- Epidermal - appear on the top layer of the skin.
- Intradermal - are formed in the deep skin layer (in the dermis).
The nevi differ from each other and appearance:
- Flat (melanocytic) - the most common and safe type of moles. In most cases, these are small smooth spots of the correct oval shape.
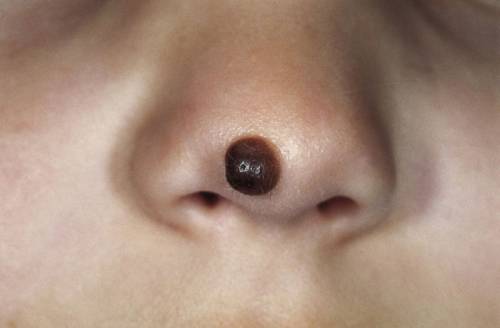
- Organoid (warty) - brown, black or blue, resembling warts in appearance, which are held on a leg and protrude above the skin. With this type of nevi, one must be careful, as it is easy to injure.
- Non-cellular (convex) - formations of a dark color, rising above the leg with a flat or rough surface, on which hair sometimes grows.
By color, red, dark and white moles are distinguished.
Red (vascular)
Appear as a result of violations in the work of blood vessels - arteries, capillaries, lymph nodes and veins. Depending on which vessel is damaged, neoplasms can be of different colors (from pink to blue-red) and sizes. Capillary moles - superficial and flat, cavernous - bumpy and nodular, embedded in the thickness of the skin.
The most common types of vascular moles are:
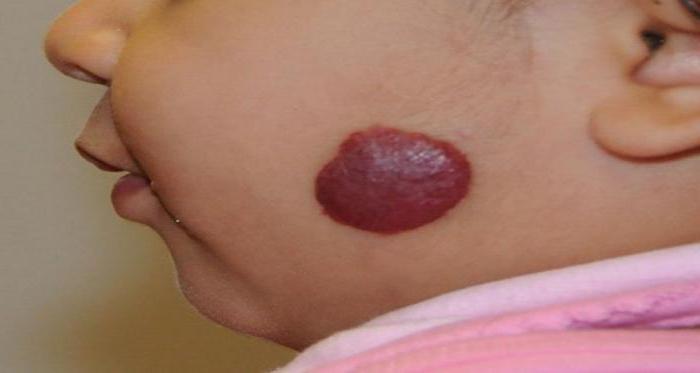
- Hemangioma (strawberry birthmark) appears in the first month of a child's life in the form of light plaques or small red swellings. Over time, the edges of the neoplasm acquire clear edges and turn red. Hemangioma usually disappears by 7 years of age.
- Malformation (stork bite and port wine spots) are congenital red moles that occur during the first weeks of a newborn's life. Due to vascular malformation, malfunctions of the blood vessels occur, which leads to the appearance of red formations on the skin. A vascular formation of a stork bite occurs in the neck, nape, forehead and temples of the baby. Its formation is associated with fetal hypoxia, which leads to squeezing of blood vessels. Such stains, unlike port wine stains, disappear on their own in the first year of a child's life.
- Port wine stains are often located on the arms, face and torso. They do not disappear with age, but only change their color and become darker in color.
Dark (non-vascular)
This type of mole appears from excessive production of melanin (coloring pigment). The formations are multiple or single plaques of various colors (gray, blue, brown, etc.) and shapes with a keratinized surface.
There are the following safe types:
- Lentigo is a common type of pigmented formations, with an equal color ranging from pale brown to brown.
- Mongolian spots - neoplasms are round pigment spots of a blue hue, which are localized in the sacral and lumbar zone. Before the age of 15, they disappear on their own without treatment.
- Coffee spots are flat, small brown moles. The presence of two neoplasms does not belong to the pathology, more than 3 - observation and additional diagnostics are required, since they can be a sign of neurofibromatosis (the tumor is formed from nerve cells).
White
This type of mole appears when the production of melanin decreases. Innovations may have different surface(rough or smooth) and dimensions. Sometimes light nevi are signs of serious illness, but in most cases, white moles are idiosyncrasy human skin, not hazardous to health.
Which are dangerous
Some types of moles are able to degenerate into malignant tumors. These include:
- Blue nevus - a round dense knot without hair, blue or dark blue, up to 5 millimeters in size. The place of localization of the mole is the face, buttocks and limbs.
- Nevus of Ota is a large pigmented formation on the face of a dark brown or blue-gray color. It is localized on various parts of the face (cheeks, cheekbones, upper jaw) and has light layers, which creates the effect of dirty skin.
- Dubreuil's melanosis is a precancerous skin lesion that looks like a single spot of light brown color with uneven outlines. Gradually, such a mole increases and changes color, becoming black or dark brown. It is formed in most cases on the face and other exposed areas of the body.
- A giant pigmented nevus is a formation that has a cracked, bumpy or warty surface from gray to black. A mole grows with a person.
- Border pigment nevus - a flat dark brown or black nodule without hair with a smooth and dry surface with a diameter of not more than 10 millimeters. Basically, these dangerous moles are localized on the palms, soles or intimate areas.
- Dysplastic moles are neoplasms of various shapes with a diameter of not more than 1 centimeter. Appear on chest and buttocks. Passed down genetically.
- Papillomatous - a convex mole with an uneven surface and irregular outlines. The color ranges from light flesh to dark brown. Often occurs on the head, there may be hairs on the surface.
Diagnostics
The study of a mole allows you to determine whether it belongs to the borderline, melanocytic species or the skin formation has a different etiology.
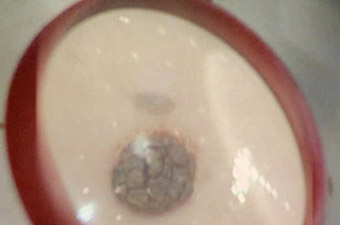
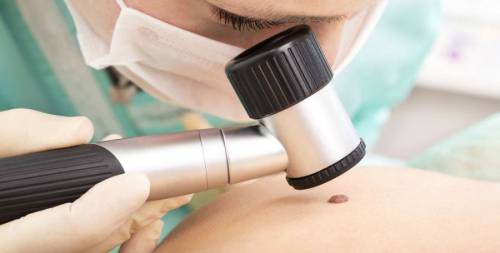
The most common diagnostic method today is dermatoscopy. The study is carried out using a dermatoscope apparatus (a microscope that magnifies the examined surface of the skin several times). During the procedure, the doctor evaluates the following signs:
- The size and color of the mole.
- edge structure.
- The presence of asymmetry.
If it is suspected that the mole is degenerating into a malignant one, a radioisotope study is performed, which refers to a non-invasive diagnostic method. The patient on an empty stomach is given to drink a preparation containing dibasic sodium phosphate, and then, using contact radiometry, the amount of the isotope accumulated in the formation and a healthy skin area symmetrical with it is compared.
There is also a thermometric diagnostic method based on the detection of pathological processes in the skin, accompanied by temperature changes. The temperature difference between the affected and healthy skin should be 4 degrees.
However, the final decision in the diagnosis of nevi is given to a histological examination, which consists in examining a sample of a skin formation obtained after the removal of a mole under a microscope. Thanks to this diagnostic method, the doctor can finally confirm or refute the malignancy of the nevus.
Removal
There are several ways to remove moles:
- Cryodestruction.
- Surgery.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Laser evaporation.
- radio waves.
The doctor selects the method taking into account the state of the neoplasm and its features, takes into account the possible risks for the patient's body as a whole.
More recently, cryodestruction and electrocoagulation were considered the main methods of removal. With cryodestruction, the mole is frozen liquid nitrogen, and electrocoagulation acts on the formation of high frequency electric current. However, these methods have side effects: the formation of blisters that appear on healthy areas of the body both after heat and after cold.
Surgical removal is carried out with ordinary brown moles, since this method allows you to completely excise all the tissues of the formation from the deep layers of the skin. Moles similar to cancer are also surgically removed for tissue histology.
For more fine procedures using radio wave coagulation. They remove moles in one motion, and this procedure lasts less than 5 minutes. The advantage of this method is that the patient can go home immediately after the operation.
Laser removal is a modern, fast and safe method leaving virtually no scars. The laser also removes warts, papillomas and benign formations.
Consequences of removal
A few hours after the removal of the mole in the wound area, there may be pain caused by a violation of the integrity of the structure of the skin. Anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs (Ketorol, Nimesulide, Nurofen, Ketanov, etc.) will help relieve pain.
The wound itself does not require special treatment and care until the sutures are removed, which is carried out for 8-10 days. After that, for the speedy healing and prevention of scar formation, it is necessary to apply ointments such as Solcoseryl, Levomekol or Methyluracil to the wound.
Until the wound is completely healed, so that inflammation and infection do not occur, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- Do not tear or wet the formed crust.
- Do not apply cosmetical tools to the wound.
- Cover the wound with adhesive tape or cloth from exposure to sunlight.
Complete healing after surgical removal of a mole occurs within 14-21 days. When using other methods of removal, wound healing is faster.
- Growing pain.
- Redness.
- The exit of pus.
- Dispersed edges of the wound.
Sometimes there is a divergence of the seams, as a result of which the edges of the wound spread and slowly grow together as it should. In this situation, you should consult a doctor who will take the necessary measures.
The child has
In most cases, the appearance of moles on the body of a child is due to a genetic predisposition. Benign formations can appear at any age: in some children immediately after birth, in others by 5-6 years.
Predisposition to skin formations appears when the baby is still in the womb. The reasons for the appearance of nevi on the body of a child are:
- Impact on the body of a pregnant woman of radiation, toxic substances.
- Hormonal fluctuations in the body of a pregnant woman.
- Predisposition of parents to the appearance of moles.
- infections urinary tract during pregnancy.
On the skin of a child, a red nevus may appear - hemangioma (vascular mole). This type of neoplasm is not dangerous and will disappear on its own after a while. A special type of skin abnormality is Setton's nevus, when a spot appears around the neoplasm. white color(skin without pigment). This may be a reaction to UV exposure or the effects sunburn. Treatment in this case is not required, after a few years the spots disappear, and the skin returns its color.
Often in children, convex moles of various colors from light brown to black appear. Such nevi are easily damaged, especially in places where they can often be injured. In this case, it is better to consult a doctor who will remove the mole.
The most dangerous complication is the malignancy of the neoplasm (melanoma, skin cancer), so parents need to regularly examine the child's moles and evaluate them according to the following signs:
- Rough edges.
- Nevus asymmetry.
- Non-uniform color.
- Large size (over 6 millimeters).
- Quick change in size.
The presence of these signs does not mean that the mole has begun to degenerate into a malignant one, but only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
During pregnancy
The appearance of a large number of moles in women who are expecting a baby is associated with hormonal changes in their body and is considered the norm.
You need to worry if a lot of moles appeared on the body during pregnancy, which began to cause inconvenience: itching, peeling, burning, they began to increase in size, change their color, shape, bleed, thicken, become convex. In this case, it is necessary to consult a doctor. Perhaps the same hormonal fluctuations are to blame, and after childbirth, the mole will again become the same size, but only a specialist can determine this.
How to remove at home
Alternative methods of treating moles involve the use of various compresses, ointments, infusions, etc. Means that do not immediately remove the nevus are considered safe, but eliminate or make it less noticeable gradually. However, in this case, it is necessary to make sure before treatment that the mole is not malignant.
If the doctor confirms that the skin formation does not threaten health in any way and carries only a cosmetic defect, then you can use one of the following folk remedies:
- Iodine. It is applied for sensitive skin. A drop of the product must be applied with a cotton swab to the nevus 2-3 times a day. The procedure should be carried out daily until improvement.
- Garlic. Stick a patch on the nevus with a hole cut out for it. Then crush the clove of garlic with a press, apply the mixture to the formation with a cotton pad, seal it with a plaster on top and leave for 5 hours. At night, this procedure is not recommended.
- Ointment from celandine and vaseline. Mix the components in a 1:1 ratio and lubricate the problem area of the skin 3 times a day.
- Vinegar essence. It is necessary to apply a drop of essence with a pipette to the mole, and carry out the procedure for 5 days three times a day.
- Compress of honey and linseed oil. Add 1 drop of linseed oil to a tablespoon of honey, moisten a gauze cloth in the mixture and apply to the skin formation for 3-5 minutes. After the procedure, gently rinse the skin. Nevus is recommended to wipe 2 times a day.
- Pineapple juice lightens dark moles. In freshly squeezed juice, you need to moisten a cotton pad and wipe the neoplasm several times a day.